Photo AI
Last Updated Sep 24, 2025
Ethical Marketing Principles Simplified Revision Notes for SSCE HSC Business Studies
Revision notes with simplified explanations to understand Ethical Marketing Principles quickly and effectively.
443+ students studying
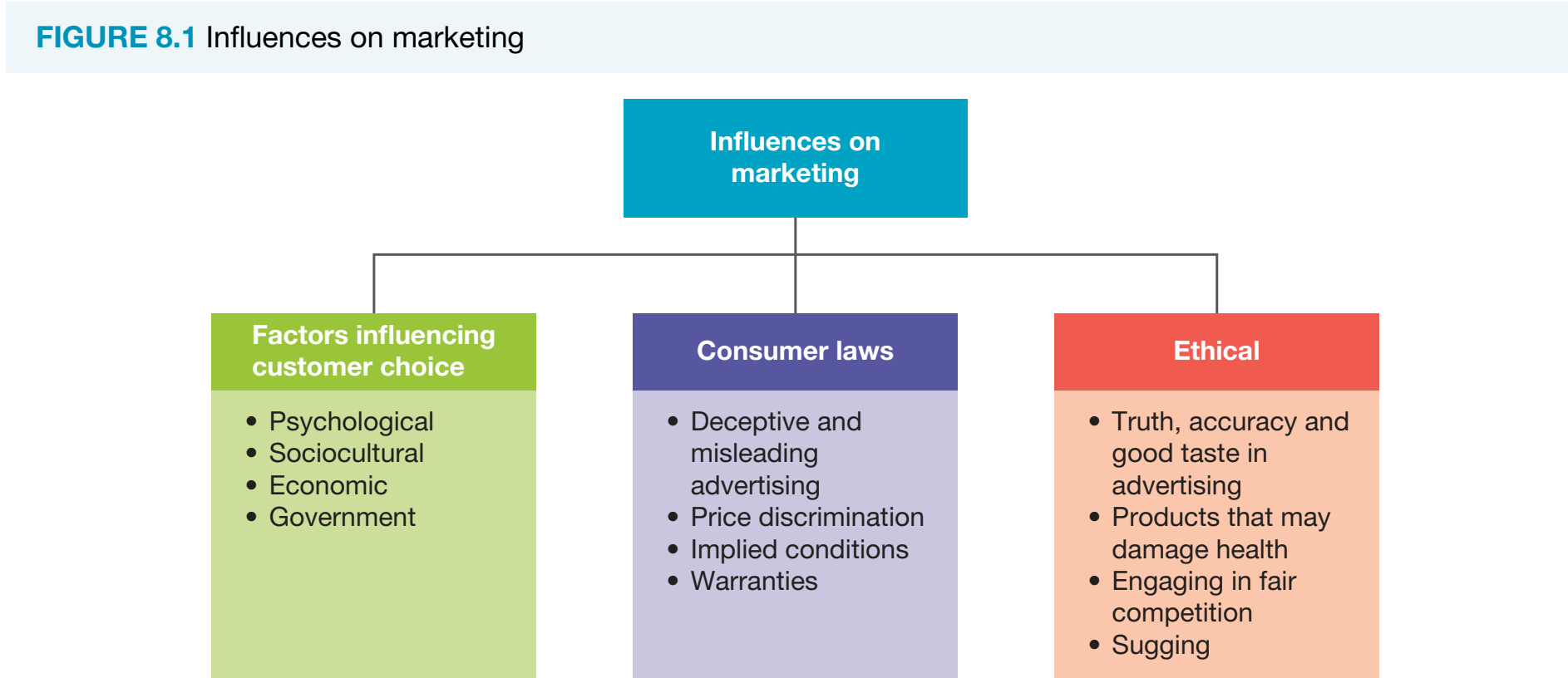
Ethical Marketing Principles
Ethical considerations in marketing are essential for maintaining consumer trust and enhancing brand reputation. This note provides an overview of ethical practices, regulatory frameworks, corporate responsibilities, and their impact on consumers and businesses.
Defining Ethics in Marketing
Marketing Ethics: Refer to the principles that guide businesses in conducting their practices in a trustworthy manner to enhance consumer trust and bolster brand reputation.
- Positive Scenario: Honest advertising involves accurately portraying products, leading to consumer satisfaction and loyalty. For example, a travel company that aligns its promotions with actual experiences typically achieves higher repeat business.
- Negative Impact: Unethical practices, such as false product claims, can damage trust. Consequences may include legal action, financial penalties, and decreased market share. A food company exaggerating health benefits might encounter fines and consumer backlash if claims are unverified.
Marketing Ethics: Are principles guiding businesses to engage in practices that build consumer trust and enhance brand reputation.
Introduction to Truth, Accuracy, and Good Taste
- Truth: Demands that advertisements accurately represent products and services.
- Accuracy: Ensures marketing messages are factually correct and properly represent offerings.
- Good Taste: Subject to cultural and societal norms, distinct from truth and accuracy.
- These principles are essential for maintaining consumer trust and adhering to regulations.
Common Pitfalls in Advertising
-
Exaggerated Claims (Puffery): Refer to legal strategies that involve exaggerated praise. Examples include claims such as "world's best coffee."
infoNotePuffery is particularly prevalent in the food and beverage industries.
-
Concealed Facts: Withholding information can mislead consumers.
infoNoteRevealing concealed facts typically erodes trust among consumers.

Overview of Main Ethical Issues in Marketing
- Truth and Accuracy: Deceptive claims result in loss of trust.
- Good Taste in Advertising: Mitigates public disapproval by aligning with societal norms.
- Health-Damaging Products: Necessitates cautious marketing of products like tobacco or energy drinks.
- Fair Competition: Promotes market variety and consumer choice.
- Sugging: Misleading consumers by masquerading sales as surveys.
Role of Regulatory Bodies and Laws
Regulatory Bodies develop and enforce marketing standards:
- Australian Association of National Advertisers Code of Ethics: Encourages honesty and prevents misleading content.
- Competition and Consumer Act 2010: Prevents deceptive practices, maintains fair competition, and imposes penalties for non-compliance.
Current Trend: Regulations in influencer marketing mandate transparency by requiring sponsorship disclosures.
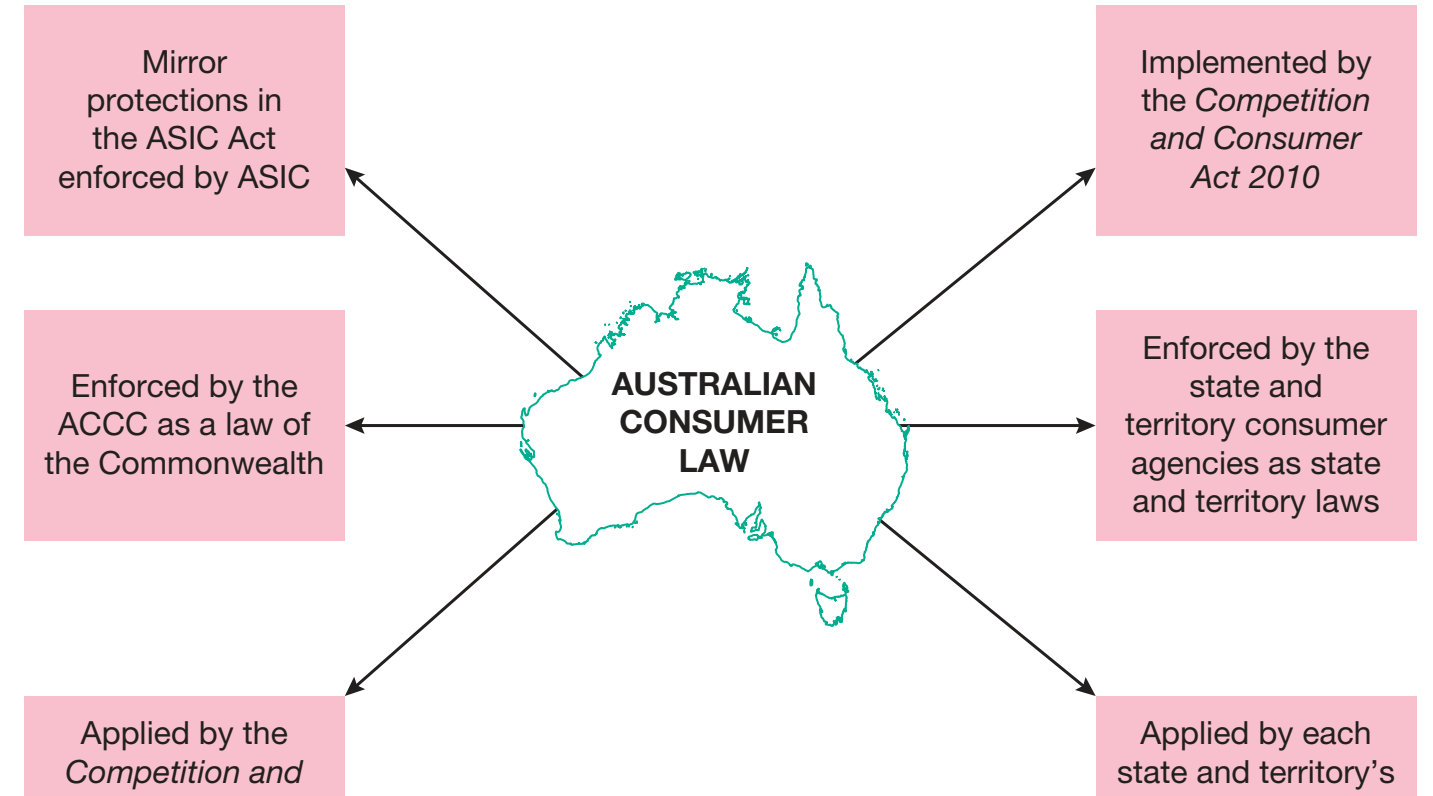
Engagement in Fair Competition
-
Fair Competition: Enables businesses to compete without deception, abiding by legal frameworks.
- Key Regulations:
- Competition and Consumer Act 2010: Ensures market integrity and deters anti-competitive behaviour.
- Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC): Monitors compliance, with a profound impact on business operations.
infoNoteKey Benefits of Fair Competition:
- Fosters innovation.
- Expands consumer choice.
- Enhances market efficiency.
- Unethical Competitive Practices:
- Price Fixing and Predatory Pricing: Price agreements undermine market fairness.
- Misleading Product Comparisons: Lead to erroneous consumer decisions.
chatImportantConsequences of Unethical Practices: Imposition of legal penalties and harm to company reputation.
- Key Regulations:
Importance of Embedding Ethical Principles in Corporate Culture
Corporate Culture: Reflects the values and practices guiding ethical marketing.
-
Strategies:
- Leadership Commitment: Advocates for ethical marketing strategies.
- Training: Ensures staff remain informed about standards.
- Policy Reinforcement: Embeds ethics through motivational incentives.
chatImportantEmbedding ethics into corporate culture is vital for sustainable success.
Overview of Ethical Concerns and Impact on Society
-
Consumer Health Priority vs. Profit Motives: Manifests in ethical dilemmas when companies prioritise profit over health.
infoNoteExamples showcase the ethical challenges of marketing harmful products.
-
Impact on Society: Products like tobacco and alcohol contribute to increased healthcare costs.
Conclusion on Sugging
Sugging: A strategy disguising sales as surveys. It raises ethical concerns due to its deceptive nature.
Sugging diminishes trust and leads to reputational harm. Compliance and transparency are of utmost importance.
Worked Example: Identifying Ethical Issues in Marketing
Consider a chocolate company that advertises its product as "helping children concentrate better at school" without scientific evidence:
- Ethical Issue: Making unsubstantiated health claims
- Potential Consequences:
- Regulatory fines from bodies like the ACCC
- Consumer mistrust when claims prove false
- Potential legal action from parents who purchased the product based on false claims
- Ethical Alternative: The company could instead focus on honest messaging about taste and quality, or invest in research to verify any health claims before advertising them
This example demonstrates how unethical marketing practices can lead to both legal and reputational damage, while ethical alternatives build sustainable business success.
500K+ Students Use These Powerful Tools to Master Ethical Marketing Principles For their SSCE Exams.
Enhance your understanding with flashcards, quizzes, and exams—designed to help you grasp key concepts, reinforce learning, and master any topic with confidence!
140 flashcards
Flashcards on Ethical Marketing Principles
Revise key concepts with interactive flashcards.
Try Business Studies Flashcards15 quizzes
Quizzes on Ethical Marketing Principles
Test your knowledge with fun and engaging quizzes.
Try Business Studies Quizzes64 questions
Exam questions on Ethical Marketing Principles
Boost your confidence with real exam questions.
Try Business Studies Questions3 exams created
Exam Builder on Ethical Marketing Principles
Create custom exams across topics for better practice!
Try Business Studies exam builder24 papers
Past Papers on Ethical Marketing Principles
Practice past papers to reinforce exam experience.
Try Business Studies Past PapersOther Revision Notes related to Ethical Marketing Principles you should explore
Discover More Revision Notes Related to Ethical Marketing Principles to Deepen Your Understanding and Improve Your Mastery
