Photo AI
Last Updated Sep 24, 2025
The Employment Contract Simplified Revision Notes for SSCE HSC Business Studies
Revision notes with simplified explanations to understand The Employment Contract quickly and effectively.
276+ students studying
The Employment Contract
Introduction
Employment Contract: A legally enforceable agreement between an employer and an employee that outlines the terms of their working relationship. This document is essential for setting clear expectations, safeguarding rights, and resolving conflicts.
Significance of Employment Contracts:
- Clarifies expectations
- Safeguards rights of both parties
- Provides a structure for conflict resolution
Employer Obligations
Providing Work
- Employers are required to provide work opportunities as per the agreed terms.
- Failure to do so may result in breach of contract claims.
Paying Agreed Income
- Wages and salaries must be paid in a timely manner.
- Non-payment can lead to claims for unpaid wages.
Safe Working Environment
- Employers must ensure a safe workplace environment.
- Negligence may result in fines and legal consequences.
Non-compliance with employment laws can lead to serious penalties, including fines and lawsuits.
Employee Obligations
Confidentiality
- Employees must maintain the confidentiality of company information.
- Breaches can have serious repercussions.
Adherence to Lawful Directions
- Adherence to reasonable employer instructions is expected.
- Non-compliance may result in disciplinary actions.
Performance of Duties
- Employees are expected to perform tasks competently and in good faith.
- They must meet productivity standards and maintain quality.
Duty of Care and Legal Implications
- Duty of Care: A mutual responsibility of employers and employees.
- Employers ensure workplace safety and adherence to legal standards.
- Employees comply with safety procedures and report hazards.
Balance of Rights and Obligations

- Rights include fair remuneration and a safe work environment.
- Obligations include compliance with laws and demonstrating competence at work.
Minimum Employment Standards
Introduction to National Employment Standards (NES)
- National Employment Standards (NES): Provide a basic safety net for employee rights, ensuring fair treatment across various industries.
Detailed Overview of NES Entitlements
- Maximum weekly hours: Typically capped at 38.
- Annual leave: 4 weeks per year.
- Personal/carer's leave: 10 days per year.
- Fair Work Information Statement: To be provided upon hiring.
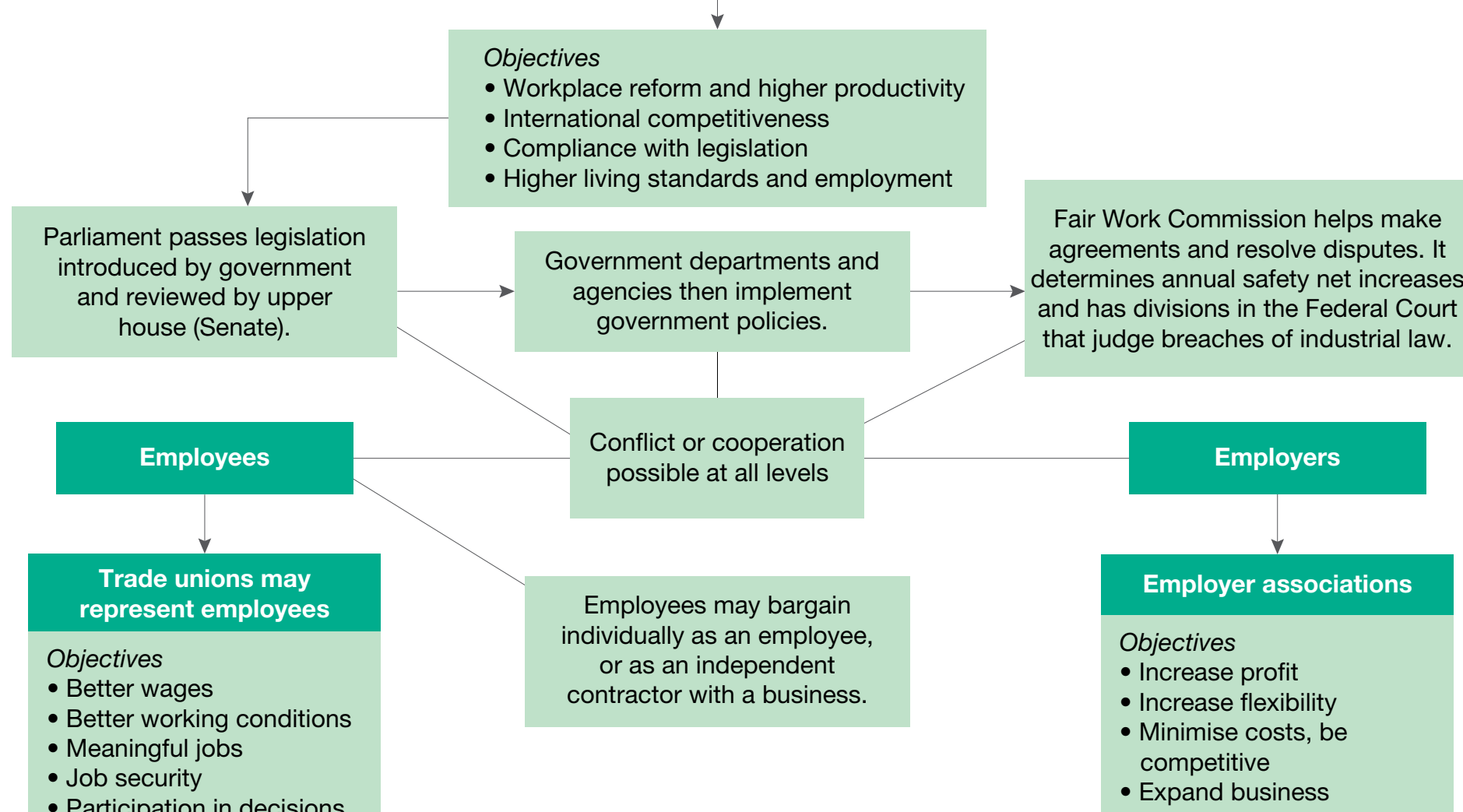
The Fair Work Commission's Role
- Oversees enforcement of NES and mediates disputes.
Overview of Employment Contracts
Types of Employment Contracts
-
Part-Time Contracts
- Pro-rata pay and benefits
- Example of flexibility: Jamie, a student who works 20 hours weekly.
-
Full-Time Contracts
- Standard working hours with comprehensive benefits
-
Casual Contracts
- Higher hourly pay, but no guaranteed hours.
-
Fixed-Term Contracts
- Defined start and end dates.
-
Freelancer Contracts
- Project-based without regular employee benefits.
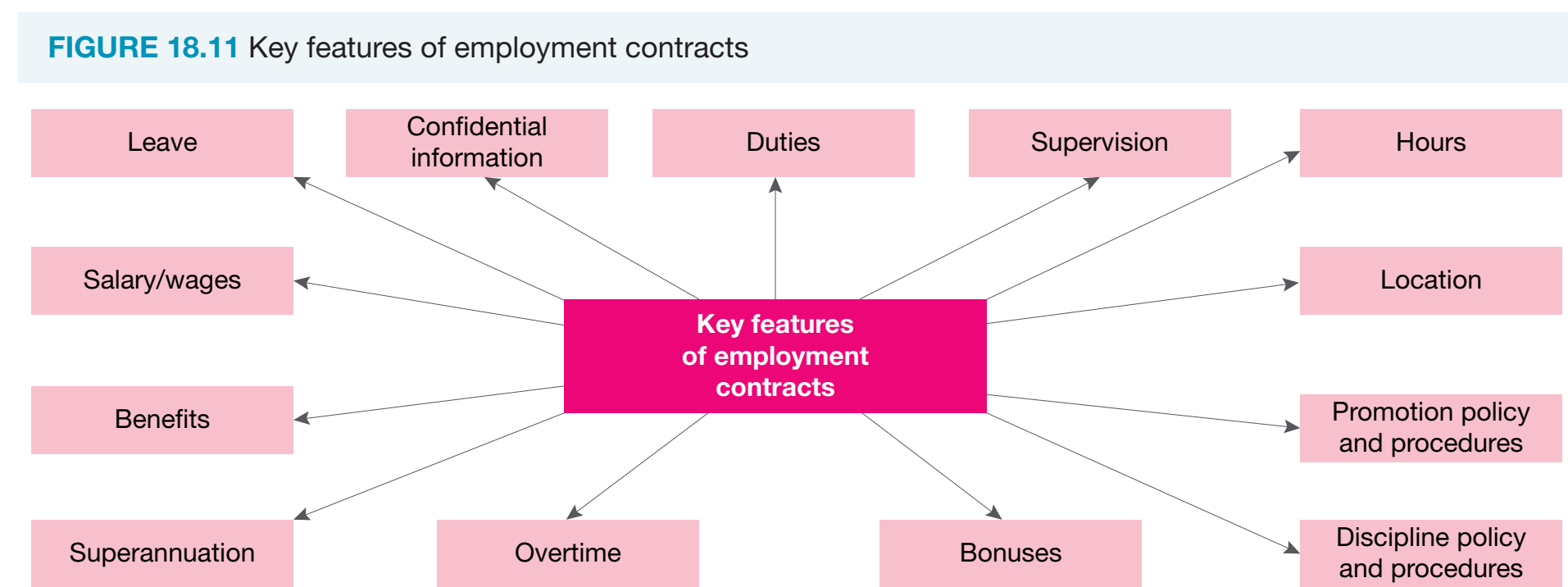
Legal Considerations
- Minimise disputes by understanding contractual terms.
- Ensure all terms are clearly documented.
- Effective communication is vital.
Proper documentation and clear communication of contract terms are essential to enforce agreements effectively.
Legal Duties under WHS Legislation
Key Duties and Risk Management
- Establish a safe working environment, provide training, conduct inspections, and foster a safety-first culture.
- Risk management involves identifying hazards, assessing risks, and implementing control measures.

Overview of EEO and Anti-discrimination
Legislative Protections
- Anti-discrimination laws promote equality and fairness.
- Key legislations include the Fair Work Act 2009, Racial Discrimination Act 1975, and Sex Discrimination Act 1984.
Definition: Racial Discrimination Act 1975: Legislation aimed at eliminating racial prejudice and promoting equality.
Real-world Examples
- Implementing EEO enhances diversity, reduces complaints, and boosts morale.

500K+ Students Use These Powerful Tools to Master The Employment Contract For their SSCE Exams.
Enhance your understanding with flashcards, quizzes, and exams—designed to help you grasp key concepts, reinforce learning, and master any topic with confidence!
130 flashcards
Flashcards on The Employment Contract
Revise key concepts with interactive flashcards.
Try Business Studies Flashcards20 quizzes
Quizzes on The Employment Contract
Test your knowledge with fun and engaging quizzes.
Try Business Studies Quizzes100 questions
Exam questions on The Employment Contract
Boost your confidence with real exam questions.
Try Business Studies Questions1 exams created
Exam Builder on The Employment Contract
Create custom exams across topics for better practice!
Try Business Studies exam builder24 papers
Past Papers on The Employment Contract
Practice past papers to reinforce exam experience.
Try Business Studies Past PapersOther Revision Notes related to The Employment Contract you should explore
Discover More Revision Notes Related to The Employment Contract to Deepen Your Understanding and Improve Your Mastery
96%
114 rated
Key influences on human resource management
HRM Stakeholders
269+ studying
189KViews96%
114 rated
Key influences on human resource management
Key HRM Influences
293+ studying
200KViews96%
114 rated
Key influences on human resource management
WHS and Anti-Discrimination Laws
331+ studying
189KViews