Photo AI
Last Updated Sep 24, 2025
Operations Processes: Outputs Simplified Revision Notes for SSCE HSC Business Studies
Revision notes with simplified explanations to understand Operations Processes: Outputs quickly and effectively.
467+ students studying
Operations Processes: Outputs
Understanding Outputs in Business Operations
What are Outputs?
- Definition: Outputs refer to the products or services delivered to customers at the end of a business process. These are the completed offerings resulting from the company's operational activities.
- Consider outputs as the end products or services that reach the customer—a culmination of business efforts.
Outputs: These are the deliverables provided to customers, reflecting the business's operational success.
Importance of Outputs
- Role in Success:
- Outputs are critical for fulfilling customer needs and attaining business objectives.
- They have a direct influence on customer satisfaction and the reputation of the business.
- Enhancing Business Reputation:
- Providing quality outputs cultivates trust and encourages customer loyalty.
- This results in repeat business and positively influences brand image.
The quality of outputs is crucial for ensuring customer satisfaction and bolstering business reputation.
Quality Control in Outputs
- Quality Control Techniques:
- Inspections:
- Routine checks verify adherence to quality standards.
- Example: Examining finished products for defects prior to distribution.
- Measurement:
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) assess output quality.
- Example: Utilising customer return rates as a KPI to evaluate product quality.
- Setting Standards:
- Establishing clear benchmarks assures consistency in products or services.
- Testing and Targets:
- Applying rigorous testing protocols and setting objectives for continual improvement.
- Inspections:
The Role of Technology in Optimising Outputs
- Using Technology:
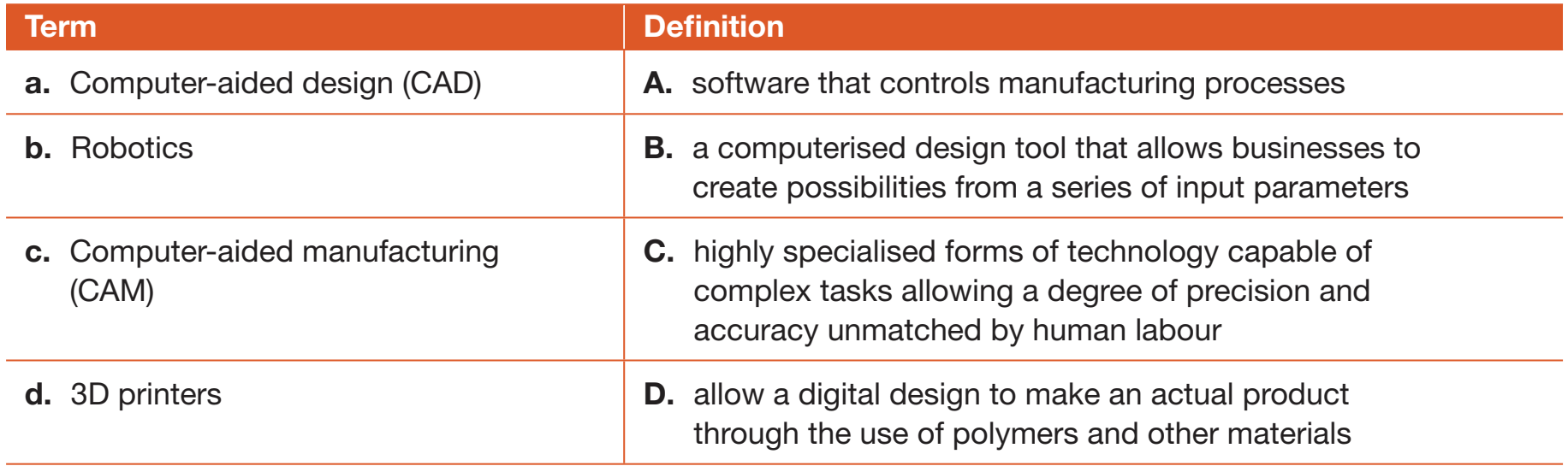
- CAD (Computer-Aided Design):
- Enhances design precision.
- Example: CAD facilitates the creation of detailed and accurate furniture designs.
- CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing):
- Guarantees consistent output quality.
- Example: In car manufacturing, CAM is employed for precise automation.
- CIM (Computer Integrated Manufacturing):
- Integrates processes, enhancing accuracy and efficiency.
- CAD (Computer-Aided Design):
Case Studies: Real-world Application
- IKEA:
- Utilises customer feedback to refine product quality.
- Result: Enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Pharmaceuticals:
- Feedback mechanisms ensure product safety and compliance with quality standards.
Sustaining high-quality outputs is crucial for continued success and maintaining competitiveness.
Customer Service Excellence
1. Definition and Significance
Customer Service: It encompasses the interactions and services provided by a business to enhance customer satisfaction and experience.
- Significance:
- Customer loyalty: Promotes repeated business and elevates the company image.
- Customer loyalty contributes to stable revenue streams.
- Repeat business: Drives increased profitability.
- Satisfied customers are more likely to return.
- Enhancing company image: Builds a robust, positive brand reputation.
- Positive interactions enhance public perception.
- Customer loyalty: Promotes repeated business and elevates the company image.
2. Key Factors Affecting Customer Service
-
Employee Interaction:
- Emphasis on positive communication, active listening, and empathy.
-
chatImportant
Effective communication intensifies customer satisfaction.
-
Customer Perception:
- Their perceptions shape their experience.
-
Training and Development:
- Ongoing training is vital for skill enhancement.
3. Effective Training Techniques
Training Programmes boost service quality and employee proficiency.
-
Workshops:
- Incorporate real-life scenarios to emulate customer interactions.
- Example: Simulate managing challenging customer dissatisfaction.
-
Role-playing:
- Equips employees for varied scenarios.
- Example: Enhance conflict resolution skills through scenario enactment.
4. Measuring Customer Service Impact
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- CSAT: Surveys assessing customer satisfaction.
- NPS: Assesses customer loyalty and likelihood of referrals.
- Retention Rates: Reflective of service efforts' effectiveness.
Utilising dashboards for KPI monitoring provides real-time insights.
5. Challenges and Solutions
-
Challenges:
chatImportantAdapting to cultural shifts and technological integration is essential.
- Cultural Shifts: Resistance to adopting customer-centric approaches.
- Technology Integration: Challenges in employing efficient CRM systems.
-
Solutions:
- CRM Utilisation:
- Employ personalised follow-ups and feedback loops.
-
infoNote
Efficient CRM systems are vital for service enhancement.
- Employee Engagement:
- Acknowledge and motivate staff for optimised performance and motivation.
- CRM Utilisation:
Technology and Customer Feedback in Improving Outputs
Overview of Technology in Output Optimisation
- Role of Technology: Technology amplifies the quality, efficiency, and innovation of business outputs, enhancing operations and competitive edge. For example, in the automotive industry, technology advances both production and design, elevating productivity.
Tech Integration
-
CAD (Computer-Aided Design):
- Definition: CAD enables precise and customisable designs through computer-assisted product creation.
- Example: Designing exact blueprints for vehicles or electronics.
- Benefits: Minimises errors and facilitates detailed customisation.
-
CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing):
- Definition: CAM automates manufacturing processes via computer software.
- Comparison: More efficient and accurate than manual methods.
- Benefits: Assures production consistency and superior quality.
-
CIM (Computer Integrated Manufacturing):
- Definition: CIM merges design and manufacturing processes using computers and automation.
- Analogy: Imagine CIM as an orchestra conductor, ensuring all production elements work harmoniously.
Enhancing Outputs Through Feedback
-
Feedback Collection: Businesses gather feedback through surveys, social media, and direct interactions.
- Example: Analysing customer reviews on social platforms to assess product reception.
-
Feedback Impact on Outputs:
- Innovation: Feedback often leads to innovative product modifications.
- Case Study: Brands such as Coca-Cola innovate flavours based on customer preferences.
Advanced Feedback Analytics
-
CRM Tools: CRM systems manage and analyse customer feedback efficiently.
- Scenario: A CRM system can monitor the frequency of customer issues with a product and assist in addressing those concerns.
-
Feedback Analytics Platforms:
- Google Analytics: Provides insights into online customer behaviour.
- Tableau: Offers comprehensible data visualisation.
Effective CRM Features
- Automation: Simplifies the process of responding to customer feedback.
- Data Centralisation: Streamlines analysis by consolidating all customer data in one place.
- Personalisation: CRM-derived information enhances customer service by tailoring interactions.
Challenges in Implementing Feedback-Based Changes
-
Financial Constraints: Budget limitations can delay changes; projecting ROI can help justify investments.
- Example: Small businesses can manage expenses by prioritising feedback that promises higher ROI.
-
Resistance to Change: Employees may resist new procedures.
- Solution: Early engagement in planning and offering incentives can facilitate transitions.
-
Complexity of Analysis: Feedback data may be overwhelming.
- Solution: Analytics tools assist in breaking down data for simpler processing.
Addressing Challenges
- Investment Justification: Presenting ROI assists in justifying initial costs.
- Change Management: Engaging employees in decision-making and providing training facilitates effective transitions.
Warranties in Business Operations
1. Definition and Types of Warranties
Warranties as Consumer Protection Tools: Warranties ensure products meet promised standards, safeguarding consumers.
Types of Warranties:
- Express Warranties: Explicit assurances regarding product quality and performance. Example: "This smartphone will reliably function for two years."
- Implied Warranties: Legal guarantees inherent in law. Example: A toaster is expected to adequately toast bread.
- Extended Warranties: Additional coverage extending beyond standard periods, typically bought separately. Example: A two-year protection plan for a refrigerator.
Understanding the Table: The table below contrasts different warranty types with examples, illustrating their unique features and offerings.

2. Legal Requirements
Laws and Obligations: Under the Australian Consumer Law (ACL), warranties must comply with specific legal standards, ensuring truthful and accurate product depictions.
-
Consumer Guarantees: Legal requirements that obligate goods to meet particular criteria:
- Acceptable quality
- Fit for purpose
- Match the description
-
Consequences for Misleading Statements: Companies making false product claims may face significant legal repercussions. Example: An electronics firm falsely advertising a waterproof camera was subject to legal action due to breach of fair trade laws.
3. Key Elements in Warranty Policies
-
Policy Elements:
- Clarity and simplicity
- Obligations for faulty products, ensuring responsible practices
-
Remedies Available:
- Repair: Utilised when a straightforward solution can resolve issues without replacement.
- Replacement: Applicable when the product repeatedly fails to function correctly.
- Refund: Preferred if neither replacement nor repair is viable or due to inherent defects.
4. Common Misconceptions
-
Warranties vs Consumer Guarantees: Warranties are specific promises made by sellers, whereas consumer guarantees are legal protections under Australian law. Misunderstanding these can affect one's awareness of their rights.
-
Refund Eligibility: Refunds are possible under circumstances such as:
- Product defects not caused by misuse
- Products that do not match descriptions
- Goods unsuitable for their intended purpose
Misunderstanding Clarification: Consumers unaware of the distinction between a warranty and a guarantee may mistakenly assume they possess fewer rights.
5. Best Practices for Warranty Policies
-
Clarity and Communication: Well-drafted warranty policies minimise misunderstandings and promote trust.
-
Building Trust and Customer Satisfaction: Transparency in warranty dealings enhances positive customer experiences and loyalty. Clearly outlining steps can strengthen trust.

500K+ Students Use These Powerful Tools to Master Operations Processes: Outputs For their SSCE Exams.
Enhance your understanding with flashcards, quizzes, and exams—designed to help you grasp key concepts, reinforce learning, and master any topic with confidence!
100 flashcards
Flashcards on Operations Processes: Outputs
Revise key concepts with interactive flashcards.
Try Business Studies Flashcards10 quizzes
Quizzes on Operations Processes: Outputs
Test your knowledge with fun and engaging quizzes.
Try Business Studies Quizzes52 questions
Exam questions on Operations Processes: Outputs
Boost your confidence with real exam questions.
Try Business Studies Questions1 exams created
Exam Builder on Operations Processes: Outputs
Create custom exams across topics for better practice!
Try Business Studies exam builder24 papers
Past Papers on Operations Processes: Outputs
Practice past papers to reinforce exam experience.
Try Business Studies Past PapersOther Revision Notes related to Operations Processes: Outputs you should explore
Discover More Revision Notes Related to Operations Processes: Outputs to Deepen Your Understanding and Improve Your Mastery
