Photo AI
Last Updated Sep 24, 2025
Supply Chain Management Simplified Revision Notes for SSCE HSC Business Studies
Revision notes with simplified explanations to understand Supply Chain Management quickly and effectively.
489+ students studying
Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management (SCM) encompasses the coordination of processes from the acquisition of raw materials to the delivery of products to consumers. It is pivotal in optimising operations, minimising costs, and improving customer satisfaction.
Introduction to Supply Chain Management
Definition and Importance
-
Supply Chain Management (SCM): The strategic coordination of activities from sourcing raw materials to delivering finished products to consumers.
- Optimising operations, reducing expenditures, and enhancing customer satisfaction are fundamental roles of SCM.
-
Importance: SCM is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge through efficient operations.
- Example Scenario: A retail brand utilising SCM to streamline inventory can decrease warehousing expenses by 20% and increase delivery speed by 30%.
Supply Chain Management: Enhances operational efficiency, reduces costs, and improves customer satisfaction, fostering a competitive workforce.
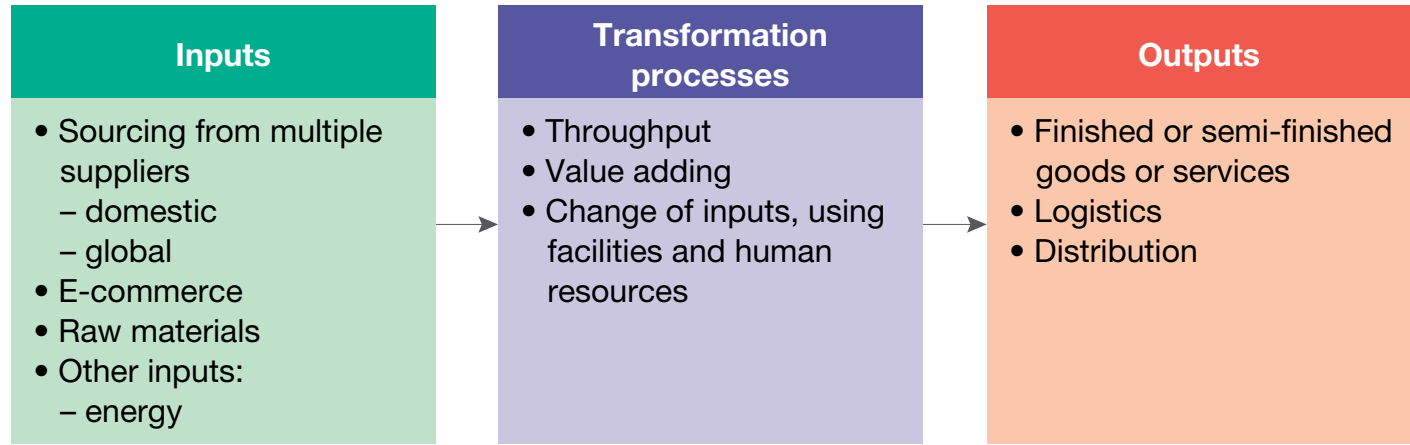
Flow of Goods, Information, and Finances
- Flow Processes:
- Goods flow: Suppliers → Manufacturers → Distributors → Retailers → Consumers.
- Information flow: Two-way flow, supporting strategic decision-making.
- Finances flow: Payments from consumers cycle back to suppliers, emphasising reverse flow.
- Seamless transitions through these stages are essential for operational efficiency.
Role and Impact of Logistics, E-commerce, and Global Sourcing
- Logistics:
- Facilitates efficient movement and storage of goods.
- Example: DHL leverages logistics operations to ensure swift delivery and reliability.
- E-commerce:
- Enables direct B2C interactions, influencing delivery and inventory strategies.
- Example: Amazon enhances customer interactions and speeds up services using advanced e-commerce technology.
- Global Sourcing:
- Involves procuring goods across borders to achieve cost savings and market expansion.
- Example: Electronics retailers source globally to provide competitive pricing and variety.
Logistics in Supply Chain Management
Logistics serves as the backbone of supply chain management, concentrating on the effective and efficient movement and storage of goods.
Introduction to Logistics
-
Broader Role: Logistics influences procurement by managing supplier relations and production by ensuring timely supply of materials. A notable example is Toyota, which uses logistics to synchronise just-in-time component delivery.
-
Key Role in Supply Chain: Boosts operational efficiency and ensures customer satisfaction through timely product delivery, while also supporting sustainability goals such as reducing environmental impact.
- Practical Impact: Streamlined logistics can cut supply chain costs by up to 15%. Savings can be reinvested in business areas such as research, development, or sustainability efforts.
Transportation Modes and Strategies
- Air Transport: Offers the fastest delivery, ideal for perishables like pharmaceuticals; though costly, it is vital for urgent shipments.
- Sea Transport: Best for bulk shipments such as grains; economical but slower.
- Road Transport: Flexible for FMCG, providing moderate speed and cost efficiency.
- Rail Transport: Cost-effective for heavy items like minerals, offering dependability over long distances.
Strategies for Selection:
- Factors to Consider:
- Delivery Timelines: Electronics companies often employ air freight for rapid market responses.
- Cost: Firms like IKEA use sea freight for large shipments to optimise costs.
- Environmental Considerations: Increasingly, companies adopt electric vehicles to reduce emissions.
Selecting the appropriate transport mode is critical. An imbalance, like prioritising cost over environmental responsibility, might harm brand reputation.
Storage, Warehousing, and Distribution Centres
- Warehousing: Suitable for long-term storage of durable items like canned foods.
- Distribution Centres: Tailored for quick turnover of items, such as seasonal apparel.
Inventory Management:
- Just-In-Time (JIT): Toyota's JIT strategy minimises storage costs by focusing on meeting immediate demand.
- Economic Order Quantity (EOQ): Balances ordering and holding expenses, saving retailers like Tesco approximately 5% on inventory costs.
Worked Example: Calculating EOQ Let's calculate the Economic Order Quantity for a retailer:
- Annual demand (D) = 10,000 units
- Ordering cost (S) = £100 per order
- Holding cost (H) = £2 per unit per year
Using the EOQ formula:
units
This means the retailer should order 1,000 units at a time to minimise total inventory costs.

Technology Integration in Logistics
- Role of AI and IoT: AI offers precise demand forecasts, while IoT guarantees real-time surveillance—crucial in cold chains for vaccines.
- Emerging Technologies: Blockchain provides potential benefits by ensuring transparency and precision throughout the logistics process.
Importance of Logistical Agility: The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the need for adaptable logistics strategies to maintain success.
Introduction to E-commerce in Supply Chain Management
E-commerce has significantly transformed supply chain management since its expansion in the late 1990s.
- Key Milestones:
- Launch of Amazon in 1995, revolutionising retail through online shopping.
- Advancement of secure online payment systems, broadening safe e-commerce access.
- Digital Infrastructure Essentials:
- Cloud Computing for scalable data storage.
- Data Analytics to support business decisions.
- Real-time Tracking enhances customer satisfaction with precise delivery information.
Importance of Digital Infrastructure: Enabling operational efficiency and competitive advantage in e-commerce.
Impact on Logistics and Distribution Strategies
E-commerce reshapes customer expectations and drives new logistics and distribution strategies.
- Last-Mile Delivery Strategies:
- Amazon employs local delivery partners and drones to improve delivery speed and coverage.
- Walmart utilises store fulfilment centres to refine distribution.
Shift Summary: Traditional logistics focused on bulk shipments, whereas e-commerce logistics meet the demand for small parcel, on-demand deliveries.
| Traditional Logistics | E-commerce Logistics |
|---|---|
| Bulk shipping | Small parcel delivery |
| Fixed delivery schedules | On-demand delivery |
Implementation of E-procurement Systems
E-procurement leverages electronic systems to streamline and enhance supply chain procedures.
Revolutionary Impact: E-procurement fosters supplier integration and shortens lead times, resulting in faster and more dependable deliveries.
Warehousing Strategies to Accommodate Online Demands
Decentralised fulfilment centres have evolved to tackle e-commerce challenges.
Fulfilment Benefits: By decentralising, companies reduce logistics costs and increase service flexibility.
| Traditional Warehousing | E-commerce Fulfilment |
|---|---|
| Centralised locations | Decentralised micro-fulfilment |
| High stock levels | Dynamic inventory management |
Influence on Global Sourcing
E-commerce revolutionises global trade engagement for businesses.
Global Reach: Opens new market opportunities, extending business operations beyond local constraints.
Challenges in Supply Chain Management
Supply chains are complex systems facing substantial challenges. These challenges influence dependability, efficiency, and costs, impacting overall performance.
Common Challenges
-
Supply Chain Disruptions: Natural disasters, geopolitical issues, and pandemics cause unforeseen interruptions.
- Example: The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted global supply chains, emphasising the necessity for resilience.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to international trade laws is crucial to avoid penalties.
Compliance: The requirement to follow trade laws and regulations to prevent penalties.
- Rising Logistics Costs: Escalating fuel prices and labour shortages drive up costs, diminishing efficiency.
- Addressing Logistical Challenges
- Technology: Utilises AI and blockchain to resolve logistical issues.
Adaptability and resilience are key for overcoming various supply chain challenges.
Practice Question: Supply Chain Disruption How can a supply chain adapt to sudden disruptions?
Solution: A supply chain can adapt to sudden disruptions by:
- Implementing robust risk management strategies
- Diversifying supplier networks across different regions
- Maintaining buffer inventory for critical components
- Developing alternative transportation routes and modes
- Using predictive analytics to anticipate potential disruptions
- Creating flexible manufacturing capabilities to adapt production
Practice Question: Technology in Supply Chain Which technologies can effectively manage supply chain disruptions?
Solution: Effective technologies include:
- AI and machine learning for predictive analysis and early warning systems
- Blockchain for enhanced visibility and traceability across the supply chain
- Internet of Things (IoT) for real-time monitoring of goods and conditions
- Cloud-based platforms for collaborative planning and response
- Digital twins for scenario planning and testing disruption responses
- Advanced analytics for quick decision-making during disruption events
E-commerce Related Challenges
- Operational Complexity: Integrating e-commerce with traditional systems introduces operational complexities.
Sustainability in Supply Chain Management
Sustainability in supply chain involves practices ensuring environmental health, social fairness, and economic viability.
Sustainability: Practices that are ecologically, socially, and economically sustainable.
Sustainable Logistics
-
Strategies for Reducing Environmental Impact:
- Energy-efficient vehicles: Deploy electric delivery fleets to reduce emissions.
-
Example: Tesla employs electric trucks, significantly decreasing carbon emissions.
Renewable Energy and Warehousing
- Utilisation of Renewable Energy:
- Community solar projects can power warehousing operations.
Conventional logistics contribute to pollution significantly. Sustainable logistics can mitigate this impact.
Green Supply Chain Initiatives
Green Supply Chain: Focuses on implementing environmentally responsible practices in every supply chain stage.
- Collaborations:
- Establish partnerships with eco-friendly suppliers to enhance sustainability.
500K+ Students Use These Powerful Tools to Master Supply Chain Management For their SSCE Exams.
Enhance your understanding with flashcards, quizzes, and exams—designed to help you grasp key concepts, reinforce learning, and master any topic with confidence!
400 flashcards
Flashcards on Supply Chain Management
Revise key concepts with interactive flashcards.
Try Business Studies Flashcards45 quizzes
Quizzes on Supply Chain Management
Test your knowledge with fun and engaging quizzes.
Try Business Studies Quizzes79 questions
Exam questions on Supply Chain Management
Boost your confidence with real exam questions.
Try Business Studies Questions3 exams created
Exam Builder on Supply Chain Management
Create custom exams across topics for better practice!
Try Business Studies exam builder24 papers
Past Papers on Supply Chain Management
Practice past papers to reinforce exam experience.
Try Business Studies Past PapersOther Revision Notes related to Supply Chain Management you should explore
Discover More Revision Notes Related to Supply Chain Management to Deepen Your Understanding and Improve Your Mastery
