Photo AI
Last Updated Sep 24, 2025
Eastern Europe: A Pivotal Year Simplified Revision Notes for NSC History
Revision notes with simplified explanations to understand Eastern Europe: A Pivotal Year quickly and effectively.
336+ students studying
Eastern Europe: A Pivotal Year
The events of 1989 were instrumental in transforming Eastern Europe. This period saw the collapse of long-standing regimes, influenced by movements such as Solidarity, alongside significant socio-political and cultural shifts. Understanding these events is essential to comprehend the region's transition from communism to democratic governance.
Introduction
The fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 marked a significant moment that initiated profound cultural shifts and socio-economic impacts throughout Eastern Europe. These changes were driven by developments in arts, literature, media, and economic policies.
Overview of Socio-Political Conditions Leading up to 1989
Poland
- Economic Hardships: The nation faced high inflation and food shortages, leading to widespread dissatisfaction and unrest among its citizens.
- Key Figures: Lech Wałęsa, a prominent leader of the opposition, symbolised resistance against the communist regime.
- Public Unrest: Increasing unrest laid the groundwork for major political transformations.

Germany (East and West)
- Separation: East and West Germany were distinct in political and economic systems.
- Living Standards: Disparities led to dissatisfaction in East Germany, where living standards were lower.
- Authoritarianism: The regime's repressive nature provoked public dissent.
Overview of Soviet Control in Eastern Europe Pre-1989
Following WWII, the Soviet Union firmly established its influence in Eastern Europe.
- Political Control: Communist governments were installed to enforce Soviet ideologies.
- Economic Influence: Through Comecon, the Soviet Union coordinated economic activities, ensuring adherence to Soviet economic models.
-
infoNote
Comecon: Established to manage trade and economic development and strengthen Soviet economic cohesion.
-
- Military Presence: The Warsaw Pact was crucial for maintaining Soviet dominance and countering Western influence.
-
infoNote
Warsaw Pact: A military alliance designed to balance NATO's power.
-

Formation of 'Solidarity' as a Mass Movement
- Origin and Growth: Solidarity originated at the Gdańsk Shipyard in 1980, motivated by economic decline and political oppression.
- Symbol for Democratic Change: Solidarity became an emblem of democratic change, symbolising the people's desire for reform and freedom.
The Gdańsk Agreement: This pivotal accord marked a turning point, signifying collaboration between workers and the government.
- Martial Law Imposition: Imposed in December 1981 to dismantle Solidarity, the movement persisted despite governmental efforts.
Important: Martial law remained until July 1983, causing significant disruptions to Poland's social order and daily life.
Influence on Movements in Other Eastern European Nations
The model set by 'Solidarity' inspired a wave of rebellion across Eastern Europe.
- Hungary: Initiated political reforms leading to 1989.
- Czechoslovakia: The Velvet Revolution, freeing the nation from communist rule.
- East Germany: Public dissent contributed to the historic fall of the Berlin Wall.
This marked a considerable domino effect, diminishing the Soviet's stronghold.
The Role and Influence of 'Solidarity' in Poland
'Solidarity' emerged as a formidable force challenging Soviet authority.
- Key Events:
- Strikes at Lenin Shipyard (1980): Represented a significant opposition to Communist policies.
- August Agreement: Recognised 'Solidarity,' exposing weaknesses in Soviet control.
'Solidarity' revealed vulnerabilities in the Soviet system, setting a revolutionary precedent.

Influence of Western Nations on Soviet Dominance
Western countries played a strategic role in influencing Soviet dynamics.
- Economic & Diplomatic Actions:
- Imposed economic sanctions to destabilise the Soviet economy.
- Offered diplomatic support to Polish movements, demonstrating international backing.

The Polish movements facilitated a broader geopolitical shift, weakening Soviet control through a combination of direct and indirect pressures from both inside and outside the region.
Decline of Soviet Influence
- Key Incidents: Notable incidents where the USSR refrained from using military force.
- Geopolitical Shift: These events highlighted the USSR's diminished sphere of influence in Eastern Europe.

The Berlin Wall
- Overview: Constructed in 1961. Served as a symbolic barrier of the Cold War dividing Berlin.
- Significance: Separated East (communist) and West (capitalist) Berlin.
- Purpose: Designed to prevent East German defections to the West.

The Wall epitomised the ideological conflict between communism and capitalism.
Socio-Political Climate Leading to the Fall
- Growing Discontent: Economic hardships combined with a lack of freedoms led to increased dissatisfaction.
- Grassroots Movements: Citizens organised to demand change.
- Mass Emigration:
- May 1989: Hungary opened its border with Austria.
- Caused a substantial exodus of East Germans.
- Key Demonstrations:
- Leipzig "Monday demonstrations": Peaceful protests added pressure for reform.
The opening of Hungary's border acted as a catalyst for change.
Key Figures and Events
- "Peaceful Revolution": Non-violent actions were pivotal during the Wall's fall.
- Influential Figures:
- Egon Krenz: Attempted to implement reforms.
- Günter Schabowski: Made a crucial error during a press conference, leading to the Wall's opening on November 9, 1989.

Peaceful Revolution: Movements characterised by non-violent protests advocating for democratic reforms.
International Impacts
- Western Response: Western nations supported efforts for reunification.
- Media's Role: Global media amplified demands for reform and freedom.
Immediate and Long-term Consequences
Immediate Effects
- Public celebrations commenced as individuals dismantled the Wall.
- Mass Celebrations: Thousands participated using hammers and chisels to chip away the Wall.
- Symbols of Unity: Dancing and singing represented newfound freedom.
Steps Toward Reunification
- Diplomatic efforts cleared the path for Germany's official reunification on October 3, 1990.
Broader European Impacts
- Domino Effect: Catalysed the fall of other communist regimes.
- Iron Curtain Symbolism: The dissolution of the "Iron Curtain" highlighted a major Cold War theme.
The Iron Curtain was a metaphor for the dividing line across Europe during the Cold War.
Cultural Shifts Post-1989
-
Artistic Freedom and Expression:
- Artistic liberation resulted in a surge of experimental forms:
- Punk Music: Emerged as a symbol of rebellion and change, especially significant in the early 1990s.
- Theatre and Visual Arts: Productions focused on freedom themes and explored avant-garde concepts.
infoNoteInfluential Artists:
- Jerzy Duda-Gracz: Known for paintings like "Theatrical," reflecting the era's spirit.
- Andrzej Wajda: Directed films such as "Man of Iron," capturing currents of change.
- Artistic liberation resulted in a surge of experimental forms:
Influence of Literature and Media
- Literature as an Expression Medium:
- Literature offered a platform for societal critique and reflection:
- "The Soccer War" by Ryszard Kapuściński: Investigates social changes through profound narratives.
- "House Under the Mountains" by Breyten Breytenbach: Captures personal and social transformations.
- Literature offered a platform for societal critique and reflection:
- Media Evolution:
- Press Freedom: The rise of outlets like Gazeta Wyborcza signified enhanced journalistic freedom.
- Milestone reports on corruption and social justice issues gained prominence.
Socio-Economic Conditions Leading to Change
-
Economic Conditions in the Late 1980s:
- Eastern Europe faced significant economic challenges:
- Inflation: Surpassed 100%, severely affecting daily life.
- Unemployment: Was extensively high, leading to a strong demand for reform.
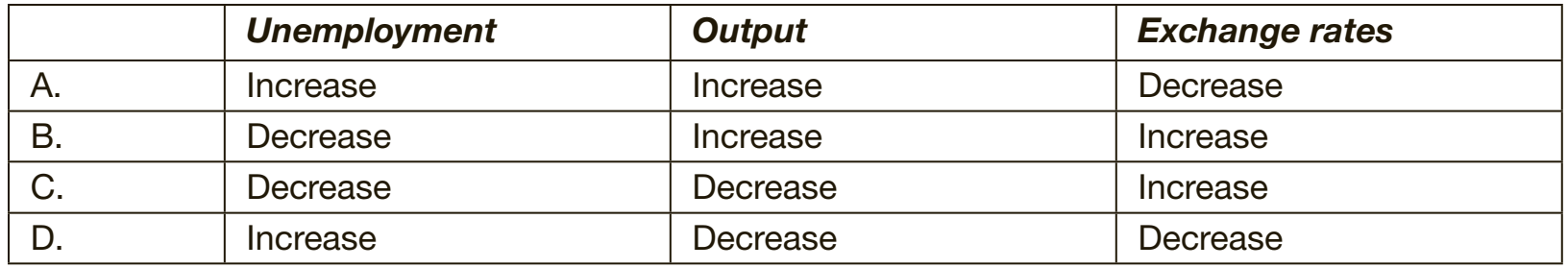
- Eastern Europe faced significant economic challenges:
-
Policies and Reforms:
- Poland's Shock Therapy:
- Implemented rapid market reforms, including:
- Price Liberalisation: Aimed at stabilising hyperinflation.
- Privatisation and market adaptations boosting economic activities.
- Implemented rapid market reforms, including:
- Poland's Shock Therapy:
Reciprocal Cultural Exchanges
-
Post-1989 encouraged vibrant cultural exchanges, fostering artistic dialogue:
- European Capitals of Culture: Events fostering intercultural collaborations and creativity.
- Artistic Renaissance:
- Influences from Western icons like David Bowie encouraged artistic innovation.
- Collaborative exhibitions reflected a blend of Eastern and Western styles.

Highlighted Impact
These transformations continue to shape Eastern European cultural scenes, blending historical traditions with global trends, fostering a rich cultural tapestry.
500K+ Students Use These Powerful Tools to Master Eastern Europe: A Pivotal Year For their NSC Exams.
Enhance your understanding with flashcards, quizzes, and exams—designed to help you grasp key concepts, reinforce learning, and master any topic with confidence!
150 flashcards
Flashcards on Eastern Europe: A Pivotal Year
Revise key concepts with interactive flashcards.
Try History Flashcards20 quizzes
Quizzes on Eastern Europe: A Pivotal Year
Test your knowledge with fun and engaging quizzes.
Try History Quizzes26 questions
Exam questions on Eastern Europe: A Pivotal Year
Boost your confidence with real exam questions.
Try History Questions1 exams created
Exam Builder on Eastern Europe: A Pivotal Year
Create custom exams across topics for better practice!
Try History exam builder90 papers
Past Papers on Eastern Europe: A Pivotal Year
Practice past papers to reinforce exam experience.
Try History Past PapersOther Revision Notes related to Eastern Europe: A Pivotal Year you should explore
Discover More Revision Notes Related to Eastern Europe: A Pivotal Year to Deepen Your Understanding and Improve Your Mastery
