Photo AI
Last Updated Sep 24, 2025
Forms of Business Ownership Simplified Revision Notes for NSC Business Studies
Revision notes with simplified explanations to understand Forms of Business Ownership quickly and effectively.
401+ students studying
Forms of Business Ownership
This revision note explores various forms of business ownership, detailing their distinct characteristics, benefits, and drawbacks.
Sole Proprietor
Definition: Sole Proprietor: An individual owns and manages a business on their own, exercising full control over business decisions.
Sole Proprietor: A business framework where one person singularly oversees and operates all facets, akin to managing a solo project at school.
Characteristics
- Single Ownership and Control: The sole decision-maker.
- Easy Management: Facilitates prompt decision-making.
- Unlimited Personal Liability: Personal assets are at risk.
- Taxation: Business earnings taxed as personal income.
Advantages
- Prompt Decision-Making
- Complete Control and Profits
- Absence of Disputes
- Potential Tax Benefits
Disadvantages
- Unlimited Personal Liability
- Restricted Growth Potential
- Higher Taxes with Increased Profits
Tax Implications

Personal Liability and Risk Management
- Obtain liability insurance.
- Keep personal and business finances separate.
Schedule regular checks to manage liabilities and remain informed on tax obligations proactively.

Partnership
Definition: Partnership: A business arrangement shared among two or more individuals managing operations together.
Partnership: A collaborative business arrangement among two or more individuals overseeing operations collectively.
Characteristics
- Joint Ownership
- Unlimited Liability
- Partnership Agreement
Advantages
- Shared Skills and Resources
- Potential for Additional Partners
- Lower Formation Costs
Disadvantages
- Unlimited Liability Risks
- Possibility of Conflicts
- Tax Liabilities
Comparison of Partnership Types
| Type | Liability | Management Roles |
|---|---|---|
| General Partnership | Unlimited | Equal participation |
| Limited Partnership | Limited for some partners | Differentiated roles |

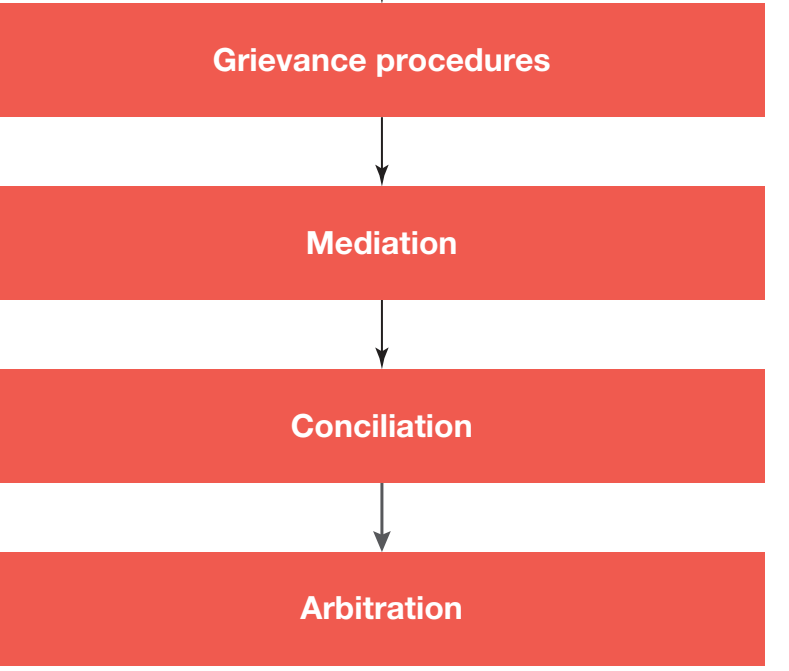
Conflict Management Strategies
- Comprehensive Partnership Agreement
- Structured Conflict Resolution Mechanisms
Close Corporation
Definition: Close Corporation: A legal business entity, separate from its members, appropriate for small businesses.
Close Corporation: A legal entity ideal for small businesses.
Characteristics
- Member-driven
- Legal Identity
Advantages
- Limited Liability
- Simplified Compliance
- Flexibility
Disadvantages
- Constraints on Capital
- Growth Limitations

Non-Profit Company (NPC)
Definition: Non-Profit Company (NPC): An organisation oriented towards promoting public benefits and social welfare.
Non-Profit Company (NPC): Prioritises social welfare over profit distribution.
Characteristics
- Board Governance
- Reinvestment of Profits
- Transparency
Advantages
- Tax Incentives
- Variety of Funding Sources
- Appeal to Talented Individuals
Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Tax Exemptions | Complex Financial Management |
| Eligible for Grants | Difficulty in Capital Acquisition |

Profit Companies
Definition: Profit Companies : are business entities designed for profit generation, focusing on maximising shareholder wealth.
Profit Companies: Entities focused on generating financial returns.
Characteristics
- Defined Legal Entity Status
- Structured Governance
Tax Implications
- Flat Tax Rate
- Double Taxation
Comparison of Subtypes

Private Company
Definition: Private Company: A business structure that emphasises confidentiality and privacy.
Private Company: A business entity that prioritises confidentiality.
Characteristics
- Shares not publicly traded
- Limited Disclosure Requirements
Advantages
- Limited Shareholder Liability
- Streamlined Management and Operations
- Enhanced Privacy
Disadvantages
- Restricted Access to Capital
- Limited Share Transferability
Personal Liability Company
Definition: Personal Liability Company (PLC): A business structure where directors' liabilities extend to personal assets.
Personal Liability Company (PLC): Extends directors' liabilities to their personal assets.
Characteristics
- Extended Directors' Liability
Advantages
- Operational Independence
- Strengthened Brand Reputation
Disadvantages
- Increased Personal Risk
Public Company
Definition: Public Company: A business entity that offers shares to the public.
Public Company: Allows public share offerings.
Characteristics
- Liquidity and Marketability
- Capacity for Capital Raising
- Transparency
State-owned Company
Definition: State-owned Company is owned and operated by the government.
A State-owned Company is a government-owned entity essential for public infrastructure.
Characteristics
- Government Ownership
- Focused on Public Service
Advantages
- Stable Funding
- Reliable Service Provision
- Public Accountability
Disadvantages
- Political Influences
- Bureaucratic Procedures
Co-operative
Definition: Co-operative: A business entity owned by a group for mutual benefit.
Co-operative: Group-owned, for shared benefits.
Characteristics
- Driven by Membership
- Autonomous
Advantages
- Community Focus
- Shared Profits
Disadvantages
- Limited Capital
- Complex Management
500K+ Students Use These Powerful Tools to Master Forms of Business Ownership For their NSC Exams.
Enhance your understanding with flashcards, quizzes, and exams—designed to help you grasp key concepts, reinforce learning, and master any topic with confidence!
90 flashcards
Flashcards on Forms of Business Ownership
Revise key concepts with interactive flashcards.
Try Business Studies Flashcards10 quizzes
Quizzes on Forms of Business Ownership
Test your knowledge with fun and engaging quizzes.
Try Business Studies Quizzes4 questions
Exam questions on Forms of Business Ownership
Boost your confidence with real exam questions.
Try Business Studies Questions4 exams created
Exam Builder on Forms of Business Ownership
Create custom exams across topics for better practice!
Try Business Studies exam builder54 papers
Past Papers on Forms of Business Ownership
Practice past papers to reinforce exam experience.
Try Business Studies Past PapersOther Revision Notes related to Forms of Business Ownership you should explore
Discover More Revision Notes Related to Forms of Business Ownership to Deepen Your Understanding and Improve Your Mastery
