Photo AI
Last Updated Sep 24, 2025
Placement Procedure Simplified Revision Notes for NSC Business Studies
Revision notes with simplified explanations to understand Placement Procedure quickly and effectively.
310+ students studying
Placement Procedure
Introduction
A structured placement procedure is essential in human resources, ensuring candidates effectively meet organisational goals, thereby enhancing both efficiency and productivity.
- Efficiency: Refines hiring processes. Organisations with structured placements see a 20% increase in workplace efficiency.
- Productivity: Aligning skills and roles leads to improved performance.
Example: Company X adopted a structured placement procedure, achieving a 25% rise in project completion rates within deadlines.
Defining Placement
Placing the Right Person in the Right Job
- Purpose:
- Aligning employee abilities with company objectives enhances productivity.
- Strategic placement maximises effective utilisation of skills.
Research indicates that strategic placement boosts performance by aligning roles with skills for better outcomes.
Matching Employee Skills and Qualifications with Job Requirements
- Job Description:
- Definition: Job Description: Outlines key responsibilities and sets clear role expectations.
- Job Specification:
- Definition: Job Specification: Details required skills, experience, and qualifications.
- Example: Specifies the competencies necessary for specific roles.
- Tools and Processes:
- Competency Frameworks: Identify skills necessary across various sectors.
- Profiling Tools: Precisely compare skills with job requirements.
| Tool | Application Example |
|---|---|
| Competency Frameworks | Used in technology to align roles with skills |
| Profiling Tools | Applied in HR for accurate role assignment |
Factors Affecting Job Descriptions
- Subjective Influences:
- Formulated through discussions with existing employees.
- Objective Measures:
- Based on data and performance metrics.
- Adaptability of Job Descriptions: They should evolve with changing business needs.
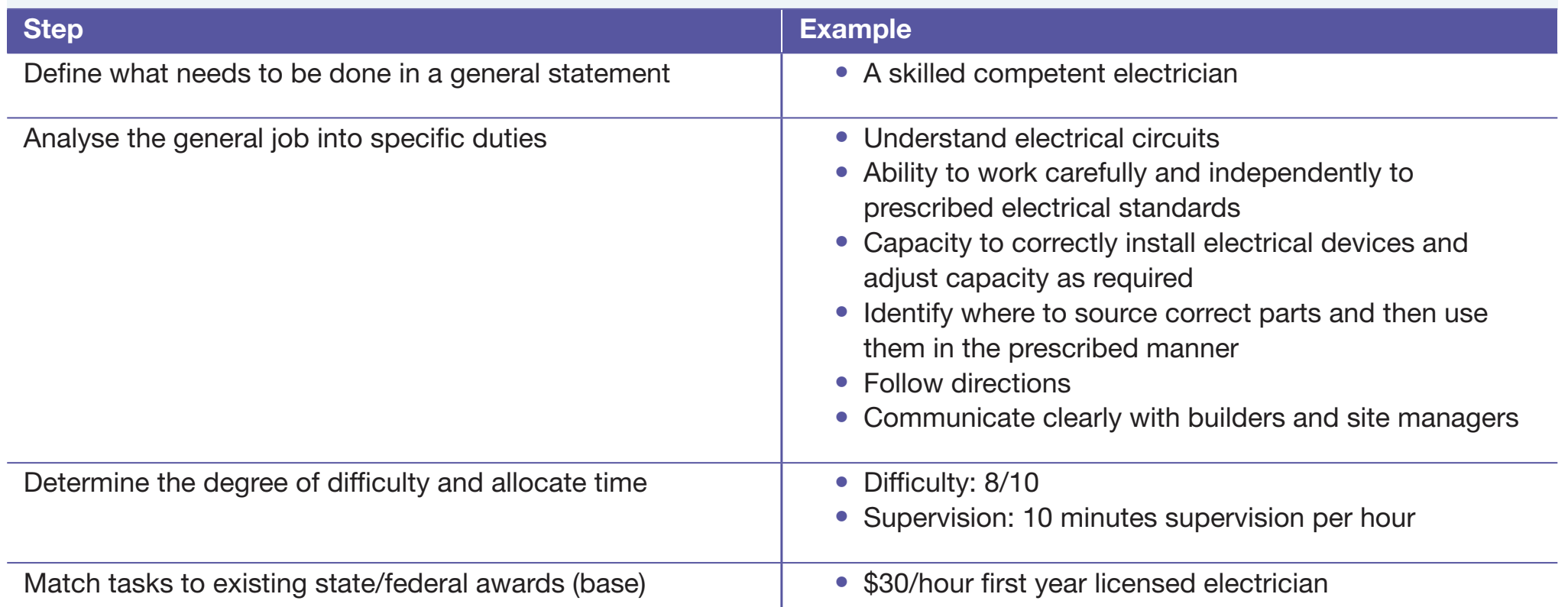
Job Analysis and Job Description
Components of Job Analysis
-
Key Role of Job Analysis in Placement:
- Identifies specific job requirements, ensuring precise placement.
- Components:
- Tasks: Specific activities required for the job. Example: IT roles require software configuration.
- Duties: Routine roles to be performed. Example: Auditors review financial documents regularly.
- Responsibilities: Obligations to be fulfilled. Example: A manager supervises team performance.
- Qualifications: Skills necessary to perform the job. Example: Accountants require a degree in finance.
-
Detailed Job Description Components:
- Elements:
- Job Title
- Summary
- Duties and Responsibilities
- Required Qualifications
- Example: Avoid mismatches by specifying necessary coding languages like Python for technical jobs.
- Elements:
Note: Job descriptions should be regularly updated to reflect organisational changes.

Legal and Ethical Standards
- Promote equity, inclusion, and fairness in job descriptions and analyses.
Checklist for Non-discriminatory Practices:
- Utilise unbiased, inclusive language.
- Maintain fairness.
- Case Example: By removing gendered language from job ads, a company increased application diversity by 30%.
Reviewing Job Requirements and Employee Qualifications
Criteria for Selection
Selection Criteria: Clearly defined qualifications and skills needed for specific roles.
- Assist in shortlisting suitable candidates who meet job specifications.
- Ensure skill-role matching is effective.
Documentation
- Resumes: Validate experience and education to avoid potential mismatches.
- Certifications: Confirm qualifications, crucial for specialised roles.
- References: Provide past performance insights, essential for reliability verification.
- Cover Letters: Indicate personality and candidate interest.
- Importance: Poor documentation can lead to misalignment and hiring unsuitable candidates.
Conducting Placement Interviews
Interview Techniques
-
Behavioural Interviews
- Use past behaviours to predict future performance.
- Example: "Describe a situation where you led a team project."
-
Situational Interviews
- Assess responses to hypothetical scenarios.
- Example: "How would you resolve a conflict with a colleague?"
Key Interview Concepts: Clarifying behavioural and situational impacts.
- Goals: Enhance decision-making by providing context on candidates' suitability.
Understanding Roles
- Role clarity importance ensures alignment with organisational goals.
- Employees who understand their duties experience a 30% higher job satisfaction rate.
Administering Placement Tests
Types of Tests
- Ability Tests: Assess cognitive skills crucial for complex problem-solving roles.
- Skill Tests: Evaluate job-specific skills through practical tasks.
- Psychometric Tests: Explore personality traits and alignment.
- Work Samples: Simulate real job scenarios.
- Medical Checks: Ensure health compliance for certain roles.
Sample Test Formats
- Multiple Choice: Common for evaluating quick reasoning abilities.
- Simulations: Measure practical skills crucial in technical roles.
- Questionnaires: Widely used in personality assessments.
Linked Test Relevance: Tests ensure candidate aptitudes match role needs.
Making Placement Decisions
Decision Criteria
- Skills: Evaluate key professional competencies necessary for success.
- Experience: Review past roles and achievements.
- Cultural Fit: Confirm alignment with the company ethos.
Scoring Systems
- Rank Ordering: Candidates are assessed based on ranking outcomes.
- Weighted Scoring: Criteria hold varying importance levels in scoring.

Ethical Considerations
- Ethics guarantee transparency and fairness.
- Adopt diversity-focused hiring strategies to minimise bias.
Types of Placement
Initial Placement
-
Purpose and Strategy: Initial placement involves assigning a new employee to their first role, crucial for defining their career path. Align their skills with organisational goals for success.

-
Checklist for Initial Placement Criteria:
- Skill match: Ensure abilities conform with role demands.
- Cultural fit: Foster smooth integration into the team.
- Growth potential: Evaluate potential for career development.
Significance of Initial Placement: Aligning roles with organizational goals greatly boosts satisfaction and productivity.
Internal Transfer
- Rationale and Benefits:
- Broadens skillsets.
- Increases networking opportunities.
- Enhances job satisfaction by providing diverse career pathways.
Promotion
- Importance and Criteria:
- Promotion involves elevating an employee to a higher position, acknowledging their contributions.
- Criteria include:
- Evaluation of performance metrics.
- Demonstration of leadership potential.
Demotion
-
Concept and Justification: Demotion entails reassigning an employee to a lower role due to performance challenges or restructuring needs.
-
Handling Demotions Constructively:
- Open Communication: Clearly discuss reasons and future expectations.
- Reassignment Strategies: Identify new roles better aligned with skills.
Transparent Management: Crucial for maintaining trust during the demotion process.
Orienting and Training New Employees
Structure of Orientation Programs
- Welcome Session: Introduce company values and expectations.
- Role-Specific Training: Provide targeted skills training pertinent to job roles.
- Mentoring: Facilitate support through experienced colleague pairings.
Each component is designed to ensure a smooth transition and enhance employee assimilation into the team.
Monitoring Employee Performance and Providing Feedback
Performance Assessments
- Utilise SMART goals to align employee activities with organisational objectives.
- Regular performance reviews essential for continuous improvement.
Feedback Mechanisms and Ongoing Assessments
- Ensure consistent communication through established feedback channels.
- Regular evaluations are vital for fostering employee growth and alignment with objectives.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Introduction to Legal and Ethical Considerations
- Objective: Ensure alignment of placement processes with legal and ethical standards.
- Significance: Emphasise the risks of non-compliance, safeguarding both the organisation and its employees.
Avoiding Discrimination in Placement
- Overview:
- Civil Rights Act: Guarantees equal opportunity regardless of race, colour, religion, sex, or national origin.
- Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA): Protects qualified individuals with disabilities.
- Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO): Essential for preventing discrimination.
Ensuring Fair and Objective Decisions
- Criteria for Objectivity: Employ clear, measurable criteria for placement decisions.
- Transparency Measures: Implement transparent decision-making processes to ensure fairness.
Compliance with Legal Frameworks
- Overview of Key Legislation
- Major Laws:
- Civil Rights Act: Prohibits discriminatory practices.
- Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA): Forbids discrimination based on disability.
- Example: A workplace offering flexible work arrangements as a form of ADA compliance.
- Major Laws:
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) in Placement
- Role and Benefits: Integrate CSR with organisational values to enhance branding.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Challenges
- Identifying and mitigating biases in decision making.
- Modernising outdated policies to reflect current standards.
Solutions
- Conduct regular HR audits and establish feedback channels.
- Implement continuous HR training initiatives.
500K+ Students Use These Powerful Tools to Master Placement Procedure For their NSC Exams.
Enhance your understanding with flashcards, quizzes, and exams—designed to help you grasp key concepts, reinforce learning, and master any topic with confidence!
230 flashcards
Flashcards on Placement Procedure
Revise key concepts with interactive flashcards.
Try Business Studies Flashcards25 quizzes
Quizzes on Placement Procedure
Test your knowledge with fun and engaging quizzes.
Try Business Studies Quizzes38 questions
Exam questions on Placement Procedure
Boost your confidence with real exam questions.
Try Business Studies Questions12 exams created
Exam Builder on Placement Procedure
Create custom exams across topics for better practice!
Try Business Studies exam builder54 papers
Past Papers on Placement Procedure
Practice past papers to reinforce exam experience.
Try Business Studies Past PapersOther Revision Notes related to Placement Procedure you should explore
Discover More Revision Notes Related to Placement Procedure to Deepen Your Understanding and Improve Your Mastery
