Photo AI
Last Updated Sep 25, 2025
Forms of Business Ownership Simplified Revision Notes for NSC Business Studies
Revision notes with simplified explanations to understand Forms of Business Ownership quickly and effectively.
464+ students studying
Forms of Business Ownership
Understanding the different types of business ownership is essential for knowing how a business is governed, managed, and how profits are allocated. Each ownership structure offers distinct advantages and challenges, which can impact a business's ability to succeed.
Definition of Business Ownership
Business Ownership: The authority to control and manage a business by individuals or entities. This determines decision-making processes and profit allocation.
Business Ownership: Defines the extent of control, decision power, and financial benefits in any business.
Types of Business Ownership
- Sole Proprietorship: Owned by an individual.
- Example: A local coffee shop operated by one person.
- Partnership: Owned by two or more individuals.
- Example: A legal firm owned by several partners.
- Close Corporation (CC): Structured flexibly for small businesses.
- Example: A family-run restaurant.
- Non-Profit Company (NPC): Focuses on a mission rather than making profits.
- Example: An organisation promoting education.
- Profit Companies:
- Private Company: Not listed on stock exchanges.
- Example: A tech startup owned by its founders.
- Personal Liability Company: Owners are personally liable for debts.
- Example: Law or accounting firms.
- Public Company: Shares sold openly on the market.
- Example: Large corporations such as British Airways.
- State-Owned Company: Managed by government bodies.
- Example: National utility providers.
- Private Company: Not listed on stock exchanges.
- Co-operatives: Managed by members for shared benefits.
- Example: A regional market organised by farmers.

Sole Proprietorship
Sole Proprietorship: The most straightforward business structure where a single person has full ownership.
- Ownership: Owned and run by one individual.
- Control: The owner independently makes business decisions.
- Liability: Unlimited liability allows personal assets to be used for settling business debts.
Advantages of Sole Proprietorship
- Complete Profit Ownership: The owner receives all earnings.
- Example: The proprietor of a neighbourhood café keeps all profits.
- Example: An online clothing seller gains all revenue and directs the venture autonomously.
- Swift Decision-Making: Decisions can be made promptly without requiring partner agreements.
- Example: An independent consultant revises project deadlines without needing permission.
- Simple Establishment: Few legal formalities required.
- Example: Starting a business by securing a local permit.
Disadvantages of Sole Proprietorship
- Unlimited Liability: Personal assets risk being used to balance business debts.
- Example: Selling personal items may be necessary to cover business losses.
- Restricted Growth Capacity: Often hard to expand due to limited resources.
- Example: A small bookshop might struggle to open additional locations because of financial limits.

- Sole Proprietorship affords full control and profit but comes with unlimited liability.
- Suitable for low-risk, small-scale operations, but less ideal for major expansions needing substantial capital infusion.
Partnership
Partnership: A cooperative agreement where two or more individuals manage a business together, dividing profits and duties.
-
General Partnership:
- All partners share equal managerial responsibilities.
- Each partner is individually accountable for the business's profits and losses.
-
Limited Partnership:
- Consists of both general partners and limited partners.
- General Partners: Run the business and assume full liability.
- Limited Partners: Invest financially and possess limited liability.

Characteristics of Partnerships
- Collective Management: Responsibilities are equally managed by partners in general partnerships.
- Liability Variation: General partners have full liability, while limited partners are protected.
- Partnership Agreement: Paramount in delineating rights and duties, mitigating disputes.
| Attribute | General Partnership | Limited Partnership |
|---|---|---|
| Liability | Complete for each partner | Limited according to investment |
| Management | By all partners | Restricted to general partners |
| Setup Requirements | Basic legal agreement | More formal filing is needed for limited partners |
Close Corporation (CC)
Close Corporation (CC): An entity with legal status, separate from its owners.
- Limited Liability: Protects members' assets from business debts.
- Credibility: Complies with similar rules as larger corporations.
- Member Constraint: Typically capped at 10, suitable for small businesses.
Limited Liability: Essential for safeguarding members' personal assets from corporate obligations.
Advantages
- Simplified Setup: CCs are established quickly and affordably.
- Management Flexibility: Members can manage directly, bypassing the need for a large board.
Disadvantages
- Member Limitation: Restricted to 10 members, potentially hindering growth.
- Financial Limitations: Smaller scale may restrict access to credit and funds.
Close Corporations vs Other Business Forms
| Feature | Close Corporations | Sole Proprietorships | Partnerships | Other Corporations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Legal Requirements | Moderate | Low | Moderate | High |
| Member Liability | Limited | Unlimited | Shared/Unlimited | Limited |
| Taxation | Corporation Tax | Personal Tax | Personal Tax | Corporation Tax |
| Operational Freedom | Flexible | High | Moderate | Structured |
Non-Profit Companies (NPCs)
Non-Profit Companies (NPCs): Organisations primarily engaged in public benefit activities without distributing profits to members. NPCs are common in educational, charitable, and community development sectors.
Legal and Structural Characteristics
-
Legal Requirements:
- Registration with appropriate bodies is mandatory.
- Needs fundamental legal documents like Articles of Incorporation.
-
Structure:
- Board of Directors: Manages governance and sets strategic objectives.
- Operational Management: Conducts day-to-day operations.
Advantages
- Tax Benefits: NPCs often enjoy tax reductions or exemptions.
- Financial Support: Qualified for grants, donations, and sponsorships.
Disadvantages
- Competition for Funds: Increasing rivalry for grants in the nonprofit sector.
- Regulatory Demands: High administrative workload to maintain tax-exempt status.
Profit Companies
Profit Companies: Aimed at generating financial returns and adding shareholder value, focusing more on profit-making rather than societal objectives.
Subtypes of Profit Companies
- Private Companies (Pty Ltd):
- Owned privately with limited shareholders, offering discretion in financial disclosures.
- Personal Liability Companies (Inc):
- Directors bear personal liability for debts.
- Public Companies (Ltd):
- Publicly traded shares providing significant capital access.
- State-Owned Companies (SOC):
- Government-run, balancing public service with profit goals.

Co-operatives
Co-operatives: An entity owned and democratically overseen by its members, designed to achieve shared economic and social objectives.
Key Characteristics
- Democracy in Decisions: Allows equitable participation through a one-member, one-vote system.
- Member Ownership: Provides individuals with ownership stakes in the cooperative.
Challenges
- Decision-making can be hindered by democratic processes.
- Revenue challenges may surface from member-centric services.
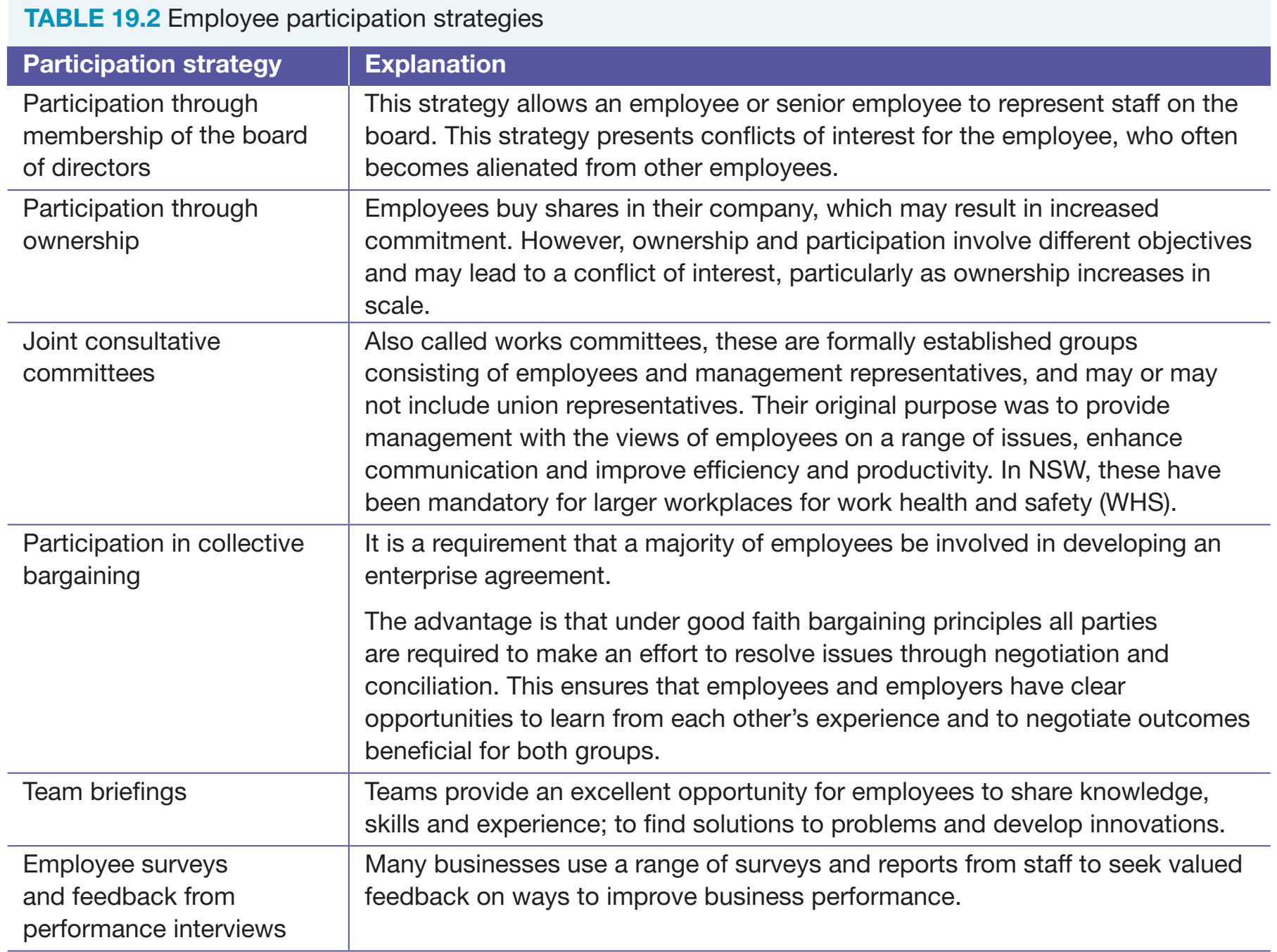
Examining Ownership Impact on Business Success
Business Success and Failure Factors
- Success Factors: Independent planning, proactive management, and financial stability are crucial.
- Failure Factors: Poor planning and mismanaged resources often lead to failure.
Capacity and Resources
- Corporations: Offer extensive growth opportunities due to a broad financial base.
- Sole Proprietorships: Limited by the resources available to the individual owner.
Management and Control
- Decision-making processes vary among ownership structures, impacting operational efficiency.

500K+ Students Use These Powerful Tools to Master Forms of Business Ownership For their NSC Exams.
Enhance your understanding with flashcards, quizzes, and exams—designed to help you grasp key concepts, reinforce learning, and master any topic with confidence!
50 flashcards
Flashcards on Forms of Business Ownership
Revise key concepts with interactive flashcards.
Try Business Studies Flashcards5 quizzes
Quizzes on Forms of Business Ownership
Test your knowledge with fun and engaging quizzes.
Try Business Studies Quizzes29 questions
Exam questions on Forms of Business Ownership
Boost your confidence with real exam questions.
Try Business Studies Questions27 exams created
Exam Builder on Forms of Business Ownership
Create custom exams across topics for better practice!
Try Business Studies exam builder54 papers
Past Papers on Forms of Business Ownership
Practice past papers to reinforce exam experience.
Try Business Studies Past PapersOther Revision Notes related to Forms of Business Ownership you should explore
Discover More Revision Notes Related to Forms of Business Ownership to Deepen Your Understanding and Improve Your Mastery
Load more notes