Photo AI
Last Updated Sep 24, 2025
TQM Fundamentals Simplified Revision Notes for NSC Business Studies
Revision notes with simplified explanations to understand TQM Fundamentals quickly and effectively.
245+ students studying
TQM Fundamentals
Introduction
- Total Quality Management (TQM): A comprehensive management approach dedicated to ensuring long-term success by meeting customer requirements.
Total Quality Management (TQM): An overarching management framework aimed at enhancing quality and performance to satisfy or surpass customer expectations.
Definition and Basics
- TQM Definition: Defined as an approach that strives to improve quality and performance to meet or exceed customer expectations.
TQM Basics Diagram
- The following diagram demonstrates TQM's core principles, focusing on continuous enhancement and employee participation:

Diagram Interpretation:
- Highlights the interconnected processes directed towards continuous improvement and employee engagement.
- Illustrates workforce participation and refinement processes as fundamental elements.
Key Principles
- Customer Focus:
- Organisations must align operations to meet and exceed customer needs.
- Essential for achieving customer satisfaction.
- Total Employee Involvement:
- All employees engage in enhancing quality.
- Encouraged through management leadership and commitment.
- Process-Centred Approach:
- Focuses on understanding and managing processes thoroughly.
- Integrated System:
- All business segments collaborate to elevate quality.
- Strategic and Systematic Approach:
- Quality is embedded as a core component of business strategies and planning.
- Continual Improvement:
- Employs methodologies like:
- PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act):
- Plan: Identify opportunities and devise a plan.
- Do: Implement changes on a small scale.
- Check: Evaluate results with data analysis.
- Act: Broaden the deployment of successful strategies.
- Six Sigma:
- Concentrates on minimising defects and boosting process efficiency.
- PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act):
- Employs methodologies like:
- Fact-Based Decision Making:
- Decisions are made based on data collection and analysis.
Fact-Based Decision Making is crucial for ensuring informed and data-driven decisions.
- Communication:
- Effective communication across all levels is fundamental.
Understanding The Impact of Poor TQM Implementation
Impact on Product/Service Quality
How Poor TQM Leads to Inferior Quality
-
Product Defects and Service Breakdowns:
- Ineffective TQM practices result in defects and breakdowns.
- Case Example: In 2014, Ford encountered production errors, leading to significant recalls due to insufficient supervision.
-
Inadequate Process Standards:
- Weak controls produce suboptimal product/service outcomes.
- Example: Amazon experienced distribution errors leading to customer dissatisfaction.
Definition Recap:
- Total Quality Management (TQM): A structured approach for enhancing quality and performance.
- Substandard Products: Items failing to meet expected criteria.
- Service Breakdowns: Failures in service delivery leading to customer dissatisfaction.
Training and Communication Deficiencies
-
Lack of Appropriate Training:
- Training is vital for maintaining quality.
- Example: Starbucks encountered quality issues as untrained baristas impacted service.
-
Poor Communication Channels:
- Effective communication avoids misunderstandings.
- A survey found 75% of quality issues stemmed from communication failures.
Impact on Customer Trust and Market Share
-
Loss of Customer Trust:
- Product/service defects diminish trust, resulting in lost customers.
- Example: Microsoft's brand value declined due to issues with software releases.
-
Market Share Decline:
- Poor quality adversely impacts brand reputation.
- The Samsung Note 7 recall demonstrated rapid market share erosion due to defects.
Studies suggest a 5% decline in customer trust can lead to a 20% market share drop, underscoring the importance of quality management.
Company Examples of TQM Failures
- Real-World Failures:
- Volkswagen's emissions scandal resulted in market penalties, highlighting TQM shortcomings.
- Analysing errors helps understand and prevent future quality issues.
Annotated Flowchart
-
A visual representation depicting how gaps in processes lead to defects.
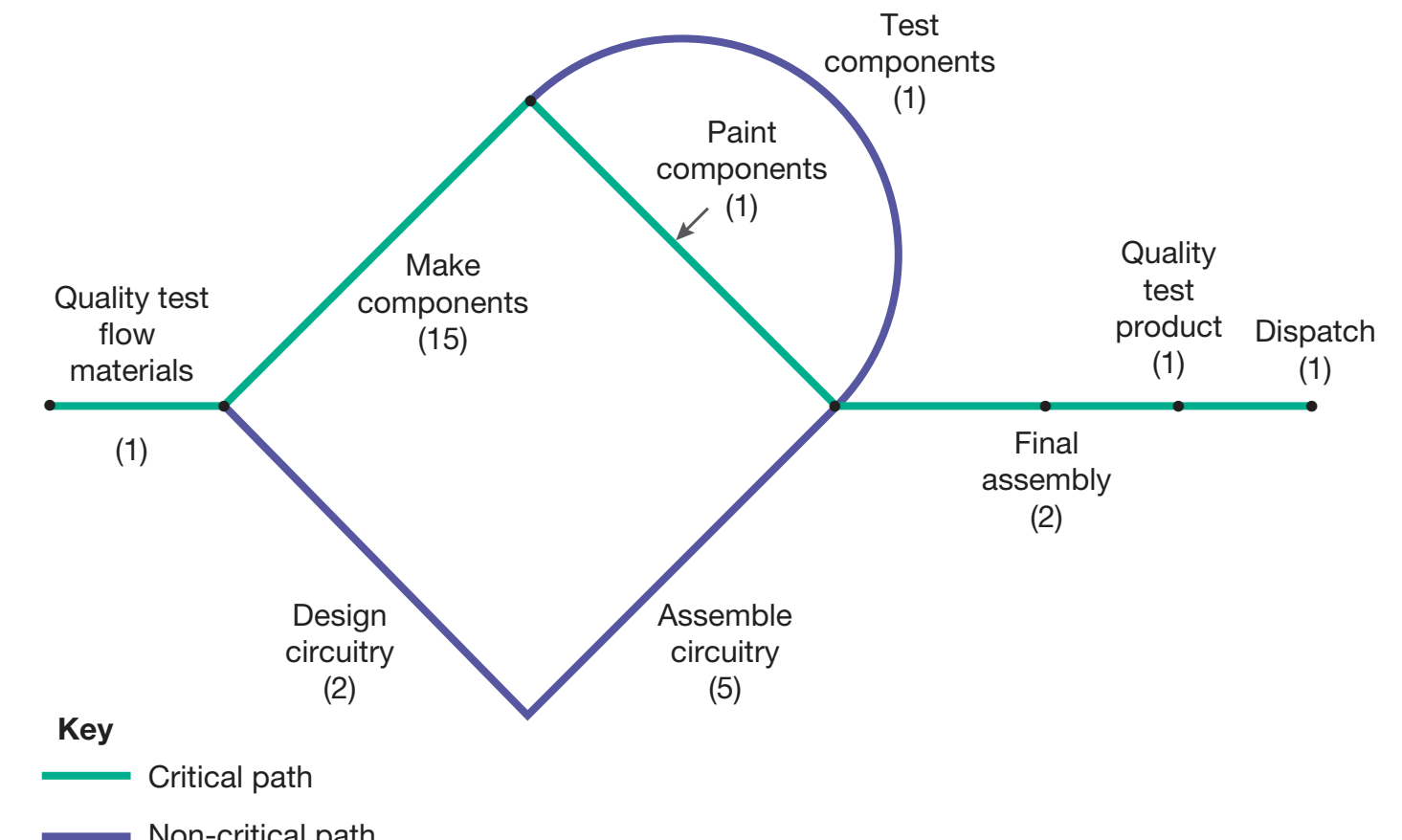
Highlight Box: Importance of Communication
Effective Communication: Zara exemplifies TQM success through improved communication, preventing failures and enhancing product quality.
Increased Costs Due to Errors and Rework
Introduction
TQM (Total Quality Management): A management strategy focusing on ensuring product quality and continuous improvement. Imagine a bakery where each baker follows the same recipe, ensuring every cupcake meets the highest quality. This exemplifies TQM. Poorly implemented TQM can lead to increased costs from errors, rework, and inefficiencies.
- Financial Consequences: Poor TQM practices elevate operational costs, such as increased expenses due to wasted ingredients when errors occur.
Increased Costs: Stem from lapses in TQM.
Understanding Financial Implications
- Diagram Analysis: A cost-benefit analysis diagram demonstrates how errors and rework detrimentally impact finances due to poor TQM.
Regular quality checks mean fewer errors and reduced rework.
Key Concepts
-
Operational Errors:
- Caused by: Deviations in processes, such as omitting a step in baking, resulting in undercooked cupcakes, indicating gaps in quality control.
-
Rework:
- Occurs: When products require correction, such as rebaking undercooked cupcakes.
- A direct result of unsuccessful TQM strategies.
Conclusion
- Consider quality practices in everyday scenarios like school projects or business operations.
- Reflective Question: How could enhancing TQM prevent errors in daily routines and streamline processes?
Connection Between TQM and Customer Satisfaction
- Effective TQM:
- Aligns processes to meet customer expectations.
- Ensures consistently high quality delivery.
- Poor TQM:
- Creates variability in quality.
- Reduces levels of customer satisfaction.
Effective TQM fosters reliable and satisfying customer experiences, while poor TQM introduces inconsistencies that can disappoint customers.
Indicators of Declining Customer Satisfaction
Understanding customer satisfaction involves monitoring specific indicators:
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Gauges customer loyalty based on the likelihood of recommendation.
- Customer Retention Rates: Reflect whether customers are remaining loyal, with low rates indicating issues.
- Complaint Levels: High complaint levels suggest critical TQM inadequacies.
These metrics are vital for evaluating TQM effectiveness. Bar graphs can visually represent changes in these indicators, demonstrating variations before and after TQM interventions.
Importance of Product Quality and Complaints
Poor TQM typically results in declining product quality, which leads to:
- Increased customer complaints.
- Loss of customer trust.
For example, if a tech company delivers faulty devices, this enhances customer frustration and service requests, ultimately reducing brand loyalty.
Role of Poor Customer Service
Inadequate TQM contributes to:
- Delays in meeting customer needs.
- Low resolution rates for issues.
- Poor quality of communication.
Prolonged Wait Times: Due to ineffective service strategies, can cause immediate customer dissatisfaction.
Real-World Examples and Customer Feedback
- Company A: Negative feedback related to delayed service and declining product standards harmed its reputation.
- Company B: Addressed customer feedback by enhancing TQM processes, gradually recovering its market position.
Feedback affects both reputation and financial outcomes through its direct impact on customer decisions.
Strategies to Regain Customer Trust
- Enhance Training: Provide staff with TQM expertise.
- Feedback Loops: Actively involve customers in the development of products/services.
- Benchmarking: Compare to competitors to identify gaps.
Companies implementing these strategies have successfully rebuilt trust by demonstrating adaptability and a commitment to quality.
Conclusion
Alignment of processes, quality consistency, and active customer feedback management are essential TQM principles. Ignoring these can diminish competitive advantage and customer trust.
Introduction to Lower Employee Morale
- Employee Morale: The overall attitude, satisfaction, and outlook within the workplace.
- Integral to TQM, as it enhances participation and continuous improvement.
Importance in TQM: Promotes a collaborative environment and boosts employee satisfaction through a focus on quality processes.
Impact of Failed TQM on Employee Morale
Failed TQM efforts can significantly lower employee morale, leading to issues such as:
- Lack of training: Leaves employees feeling unprepared.
- Poor communication: Creates frustration and misunderstandings.
- Insufficient empowerment: Makes employees feel undervalued.
- Frequent errors/rework: Increases stress for employees.
A notable case recorded a 50% rise in turnover due to failed TQM. Contributing factors included inadequate employee involvement in decisions and ineffective communication strategies.
Causes of Low Morale Due to Ineffective TQM
- Training Deficits: Insufficient resources and support.
- Scenario: Employees cannot excel without adequate resources.
- Poor Leadership Communication: Vague objectives and goals.
- Scenario: Results in misaligned efforts and objectives.
- Unrealistic Goals: Induce high pressure.
- Scenario: Employees are demotivated by unattainable goals.
- Lack of Recognition: Leads to feelings of being undervalued.
Statistics indicate approximately 30% of training initiatives fail due to unclear objectives and a lack of structure, contributing to low morale.
Impact of Low Morale on the Organisation
- Increased Error Rates: More prevalent in environments with low morale.
- High Employee Turnover: As morale decreases, the rate of departures increases.
- Reduced Productivity: Negatively affects overall efficiency and output.
According to recent studies, organisations with high morale report up to 20% fewer errors than those with low morale. Expert John Smith says, "Employee engagement is directly linked to performance and error reduction."
Strategies to Improve Employee Morale
Enhance morale through actionable strategies:
- Enhance Training Programmes: Equip employees with essential skills.
- Foster Open Communication: Promote direct feedback and inclusivity.
- Implement Recognition Schemes: Regularly acknowledge and reward contributions.
Successful Example
Numerous companies, such as XYZ Corp., have successfully implemented inclusive communication strategies, resulting in improved morale and reduced turnover.
Expert Insight
"Continuous employee support and recognition lead to increased satisfaction and productivity," states Jane Doe, a leading HR consultant.
Conclusion
- Effective TQM: Enhances morale, decreases turnover, and increases productivity.
- "Implementing effective TQM not only boosts morale but establishes the foundation for enduring business success."
Introduction
Competitive Advantage: A distinctive factor that allows organisations to outperform competitors.
- Essential for maintaining market position and profitability.
- Perpetual evolution is necessary for sustaining an edge, such as a company leading with eco-friendly products to attract environmentally-conscious consumers.
Impact of Poor TQM on Competitive Edge
Total Quality Management (TQM): A management approach dedicated to improving the quality of organisational processes.
- Poor TQM practices lead to:
- Operational inefficiencies, causing bottlenecks.
- Product inconsistencies, triggering market share losses.
- Example: "Company X" experienced a 20% revenue decline due to inconsistent quality, leading to dissatisfaction among customers and stakeholders. The issue was addressed by adopting ISO-certified TQM strategies, which reduced defects by 30%.
Competitor Analysis

- Competitor analysis reveals:
- Market opportunities capitalised on by superior performers.
- Allow strategic adjustments to address losses due to TQM failings.
- Application: In hypothetical scenarios, such analysis can guide strategic redirections in business simulations or studies.
Quality and Innovation

- Effective TQM directly enhances product quality and innovation potential.
- Poor TQM undermines differentiation strategies and diminishes sustained competitive advantage.
- Example: A technology firm experienced innovation delays, missing crucial market windows, when lacking a TQM framework, resulting in a loss of market confidence.
Customer Trust and Reputation
- Poor TQM results in:
- Trust erosion affecting brand reputation.
- Subsequent impact on sales.
- Example: "Organisation Y" encountered a 15% sales decline when defects emerged on social media, a pivotal point diminishing competitive capability.
Strategies for Reclaiming Competitive Advantage
- Proposed Strategies:
- Conduct comprehensive TQM audits with defined benchmarks.
- Learn from industry turnarounds showcasing best practices.
- Expert Quotes:
- "Embedding TQM deeply within organisational culture ensures adaptability," noted a prominent business strategist.
- Metrics: Aim for reduced defect rates as a key indicator of process quality.
Conclusion
Effective TQM mitigates risks to competitive positioning. To secure market leadership, organisations must continually adapt and enhance TQM methodologies.
Future outlook: Companies should invest in workforce TQM training, ensuring ongoing quality improvements and market adaptability.
Impact of Poor TQM on Brand Reputation
Introduction
- Focus: This section explores the reputational damage from poorly implemented Total Quality Management (TQM).
- Reputation: Overall perception from customers and stakeholders.
- Directly relates to customer perceptions and experiences.
- Vital for long-term business success.
Reputation: The collective perception customers hold of a brand or business.
Impact of Poor TQM on Brand Reputation
- Defects and Quality Control:
- Frequent product defects create negative customer experiences.
- These perceptions can detrimentally affect brand reputation.
- Social Media Amplification:
- Viral negative feedback can escalate issues swiftly.
- Platforms like Twitter and Facebook facilitate rapid dissemination of discontent.

Case Studies on Reputational Harm
- Mobile Phone Brand:
- Suffered damage due to defective batteries resulting in recalls.
- Experienced a 20% drop in market share.
- Automobile Manufacturer:
- Brake failures led to a 15% decrease in annual sales.
- Required a significant recall of one million vehicles globally.
Case Study Takeaway: Regular inspections can avert reputational crises.
Recovery Strategies
- Transparency:
- Clear and open communication helps rehabilitate trust.
- Essential for demonstrating commitment to resolving issues.
- Accountability:
- Taking responsibility through enhanced quality measures.
- Quality Improvement:
- Rigorous checks and sustained process improvements are crucial.
- Successful Turnarounds: Companies such as XYZ Corp observed a 30% increase in customer trust after a crisis.

Insights from Experts
- Continuous Improvement: The key to sustaining brand reputation recovery.
- Stakeholder Communication: Maintain direct engagement to build trust.
- Industries Highlighted: Demonstrated effective TQM utilisation in electronics and automotive sectors.
Expert Advice: "Ongoing improvement and direct stakeholder communication are vital for restoring and maintaining a strong brand reputation." – Dr. Jane Quality
- Key Takeaways:
- Engage in continuous quality assessment.
- Focus on communication and excellence in product delivery.
By employing these strategies and expert insights, businesses can effectively address and recover from reputational damage due to TQM failures.
500K+ Students Use These Powerful Tools to Master TQM Fundamentals For their NSC Exams.
Enhance your understanding with flashcards, quizzes, and exams—designed to help you grasp key concepts, reinforce learning, and master any topic with confidence!
40 flashcards
Flashcards on TQM Fundamentals
Revise key concepts with interactive flashcards.
Try Business Studies Flashcards5 quizzes
Quizzes on TQM Fundamentals
Test your knowledge with fun and engaging quizzes.
Try Business Studies Quizzes3 questions
Exam questions on TQM Fundamentals
Boost your confidence with real exam questions.
Try Business Studies Questions1 exams created
Exam Builder on TQM Fundamentals
Create custom exams across topics for better practice!
Try Business Studies exam builder54 papers
Past Papers on TQM Fundamentals
Practice past papers to reinforce exam experience.
Try Business Studies Past PapersOther Revision Notes related to TQM Fundamentals you should explore
Discover More Revision Notes Related to TQM Fundamentals to Deepen Your Understanding and Improve Your Mastery
Load more notes