Photo AI
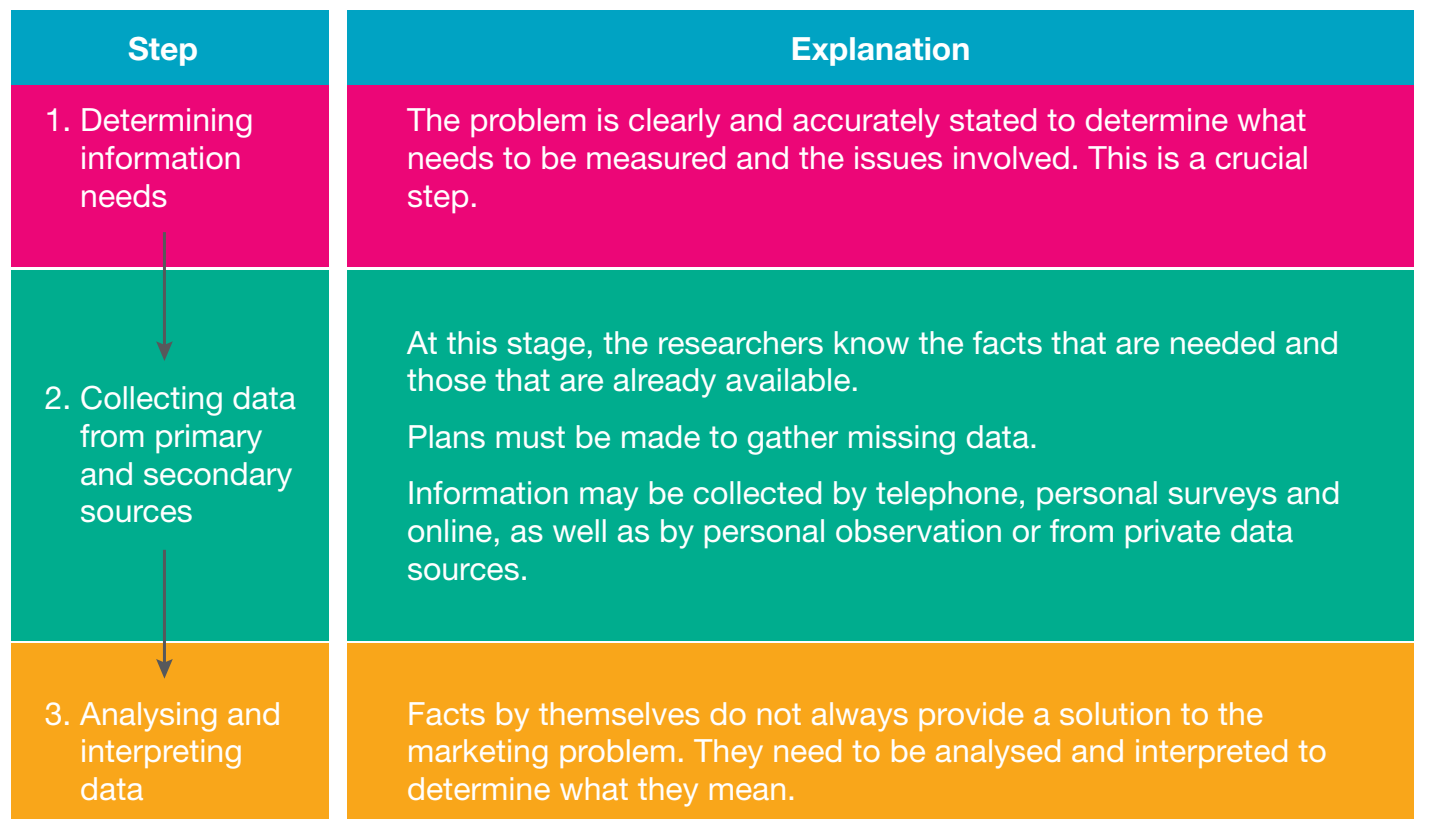
Last Updated Sep 24, 2025
Plant Defence Against Pathogens Simplified Revision Notes for SSCE HSC Biology
Revision notes with simplified explanations to understand Plant Defence Against Pathogens quickly and effectively.
200+ students studying
Plant Defence Against Pathogens
Introduction
Plants encounter numerous challenges posed by pathogens, impacting their health and survival. Understanding how plants defend themselves is crucial for maintaining ecological balance and agricultural productivity. This is particularly important in regions like Australia, where plants such as Eucalyptus and Acacia are prevalent.
Key Definitions:
Innate Immunity: Refers to the fundamental physical and genetic defences in plants against pathogens.
Adaptive Immunity: Involves plants' enhanced responses, such as systemic acquired resistance (SAR) and induced systemic resistance (ISR), to improve their defences.
Phytophthora cinnamomi: A significant source of ecological disruption, notably affecting Eucalyptus.
Phytophthora cinnamomi: Recognised for its aggressive nature and adaptability in afflicting Eucalyptus.
Importance of Plant-Pathogen Studies
Comprehending plant-pathogen interactions is essential for multiple reasons:
- Economic Significance: Agriculture depends on healthy plants, and understanding pathogens is vital to reduce crop losses.
- Ecological Impact: Native flora is crucial for ecosystems; preserving plant health supports biodiversity.
Research on plant-pathogen interactions is integral to achieving sustainable agriculture and conserving biodiversity.
Overview of Common Pathogens
Several pathogens affect Australian flora, primarily fungi and viruses:
- Fungi: Phytophthora cinnamomi causes notable harm via root rot.
- Viruses: Impact plants such as Eucalyptus and Acacia by disrupting vital functions.
Plant-Pathogen Interaction Dynamics
Entry Points
- Stomata and Wounds: These act as primary entry points for pathogens.
Infection and Colonisation
- Initial Contact & Entry: Pathogens gain access through openings.
- Colonisation: This disrupts plant harmony, causing systemic issues.

Types of Plant Defences
Physical Defences
- Thick Cuticles: Function as barriers to prevent pathogen entry.
- Bark: Offers a robust shield against pathogens, notably in Eucalyptus and Acacia.
- Small Stomata: Minimise entry points for pathogens.

Chemical Defences
- Secondary Metabolites: Compounds like phytoalexins target pathogens.
- Signalling Molecules: Salicylic acid and jasmonic acid initiate defence responses.

Plant Immune System Components
Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns (PAMPs)
- Elicit immune responses by being recognised by plant receptors.
Effector-Triggered Immunity (ETI)
- Utilises specific resistance genes to detect pathogen effectors, following the gene-for-gene hypothesis.

Environmental Influences on Plant Defences
Temperature and Precipitation
- Influence structural and biochemical defences, affecting pathogen proliferation.
Soil Characteristics
- Nutrient Availability: Correlates with the strength of defences.
- Soil Salinity: Impacts water uptake and weakens defences.
Biotic Interactions
- Symbiotic Relationships: Enhance resilience through beneficial associations.
Visual and Practical Investigations
- Sample Collection: Practice sterile techniques to avoid contamination.
- Inoculation: Introduce pathogens within a controlled laboratory setting.
Conclusion and Summary
Investigating plant-pathogen interactions deepens the understanding of plant defences and aids in developing effective conservation strategies. This is particularly crucial for sustaining agricultural practices amidst evolving environmental conditions.

Recommendation: Utilise secondary data for comprehensive insights into plant defences and broader conservation outcomes.
Review Questions
- Which of the following is NOT part of a plant's immune defence?
- Production of phytoalexins
- Activation of T-cells
Solution: T-cells are part of the animal immune system, not plants'. Plants rely on innate immunity mechanisms rather than adaptive cellular responses like T-cells.
500K+ Students Use These Powerful Tools to Master Plant Defence Against Pathogens For their SSCE Exams.
Enhance your understanding with flashcards, quizzes, and exams—designed to help you grasp key concepts, reinforce learning, and master any topic with confidence!
100 flashcards
Flashcards on Plant Defence Against Pathogens
Revise key concepts with interactive flashcards.
Try Biology Flashcards9 quizzes
Quizzes on Plant Defence Against Pathogens
Test your knowledge with fun and engaging quizzes.
Try Biology Quizzes38 questions
Exam questions on Plant Defence Against Pathogens
Boost your confidence with real exam questions.
Try Biology Questions1 exams created
Exam Builder on Plant Defence Against Pathogens
Create custom exams across topics for better practice!
Try Biology exam builder24 papers
Past Papers on Plant Defence Against Pathogens
Practice past papers to reinforce exam experience.
Try Biology Past PapersOther Revision Notes related to Plant Defence Against Pathogens you should explore
Discover More Revision Notes Related to Plant Defence Against Pathogens to Deepen Your Understanding and Improve Your Mastery
